Numerical integration
TME 310 - Computational Physical Modeling
University of Washington Tacoma
Integrals
An integral is a function or value that describes:
- The inverse of the derivative
- The area under a curve
- The accumulation of change
- It can be
- indefinite: \(\displaystyle \int f(x) \,dx = F(x)\)
- definite: \(\displaystyle \int_{a}^{b} f(x) \,dx = F(b)-F(a)\)
Integrals
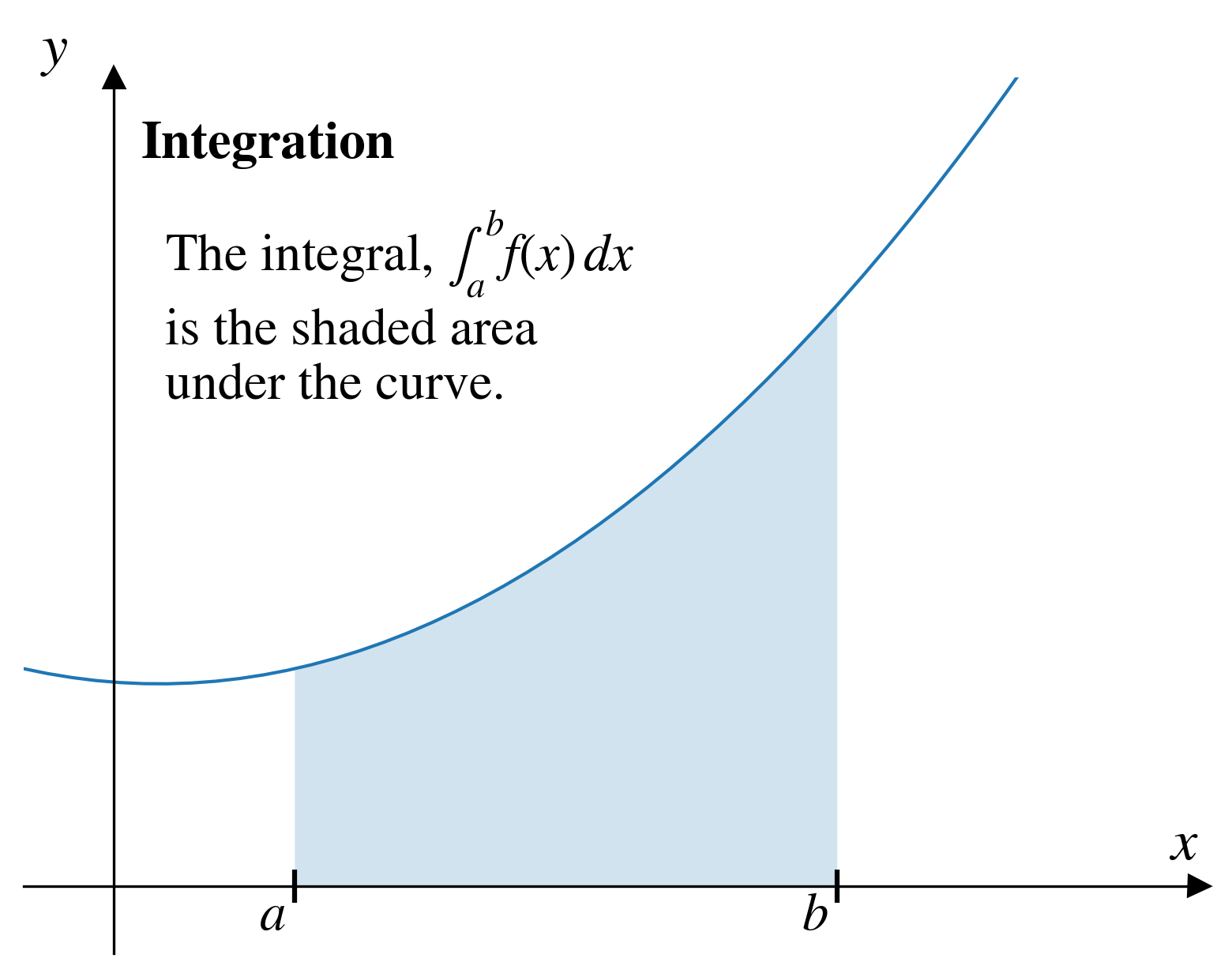
Approximating integrals
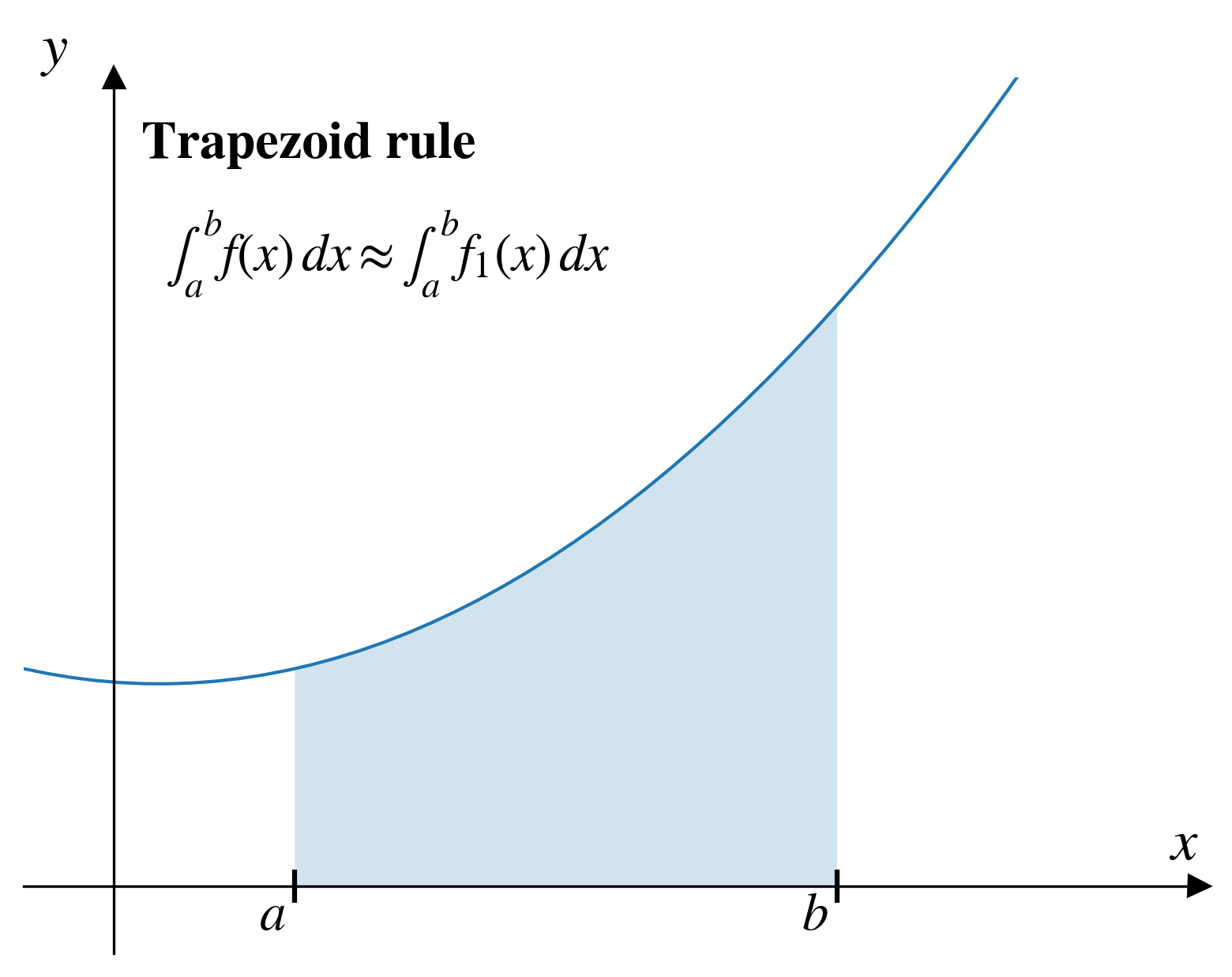
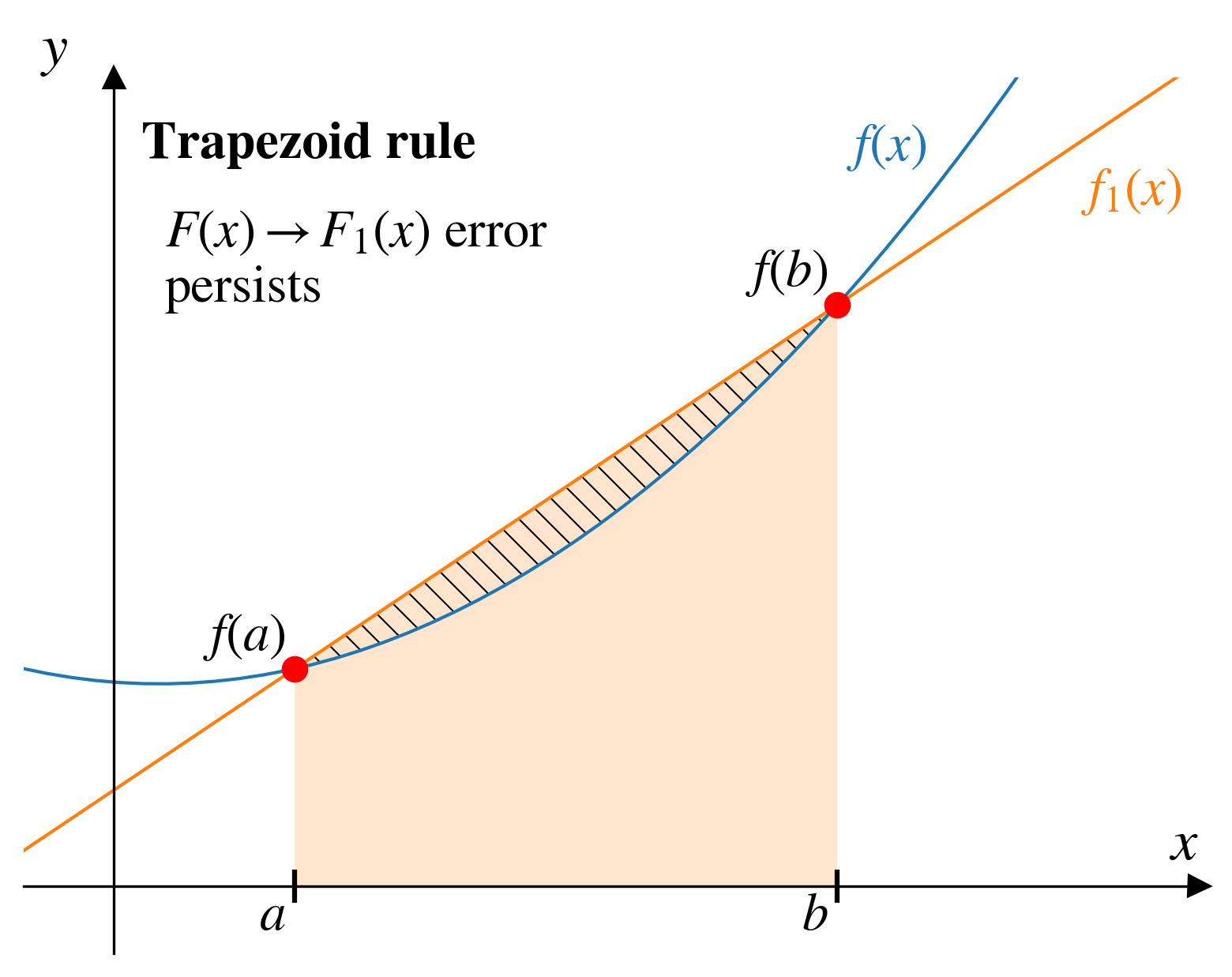
In numerical integration approximate the integral of a function, \(f(x)\) by finding the integral of a simpler function \(f_n(x)\).
If we assume that the simpler function is a straight line (which we’ll call \(f_1(x)\)), we can approximate the integral using the trapezoid rule.
Trapezoid rule (part 1)
\[\int_{a}^{b} f(x)\,dx \approx \int_{a}^{b} f_1(x)\,dx\]
where
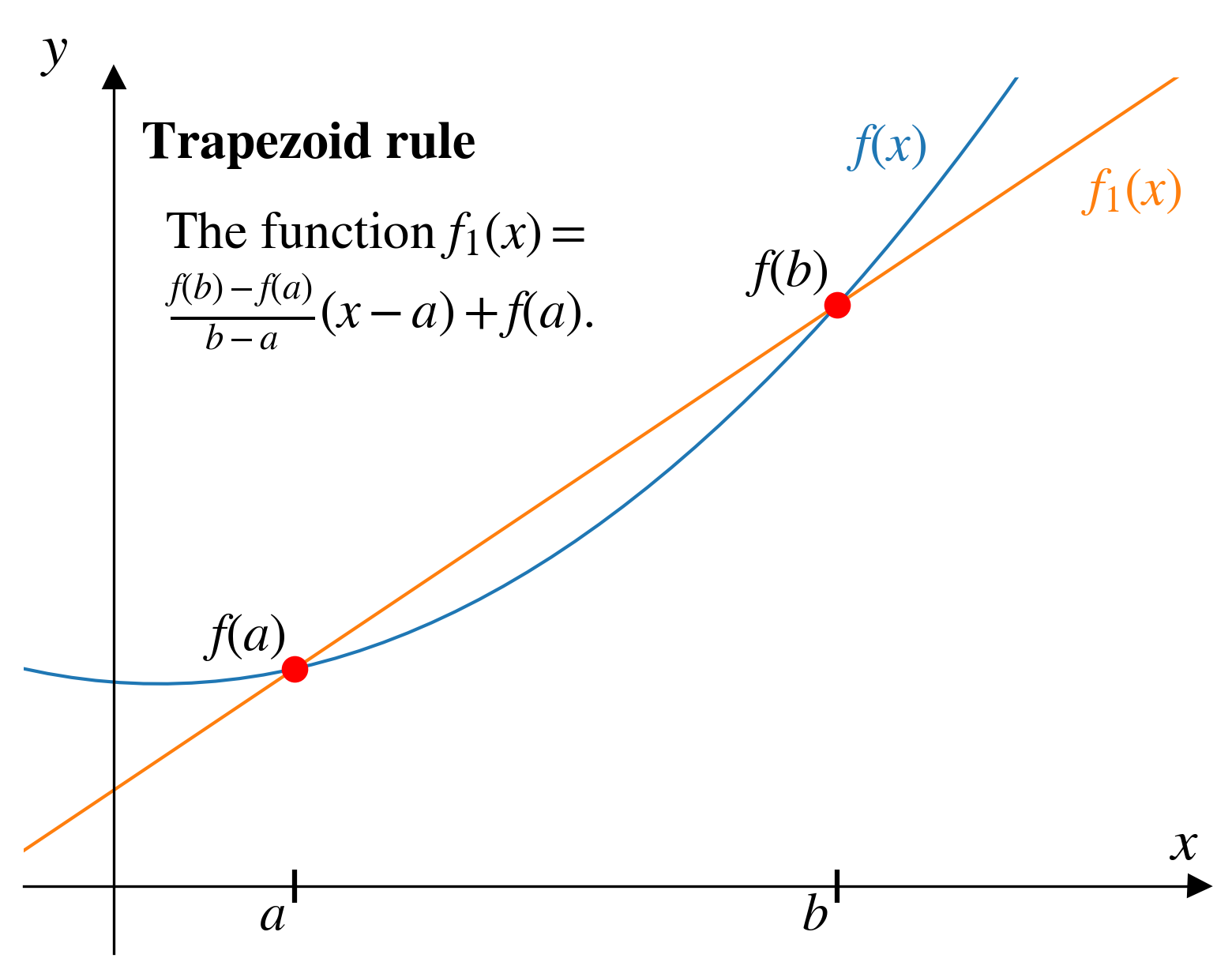
\[f_1(x) = \frac{f(b) - f(a)}{b-a}(x-a)+f(a)\]
\(f_1(x)\) is just the equation of a straight line that intersects \(f(x)\) at the points \(a\) and \(b\).
Trapezoid rule (part 2)
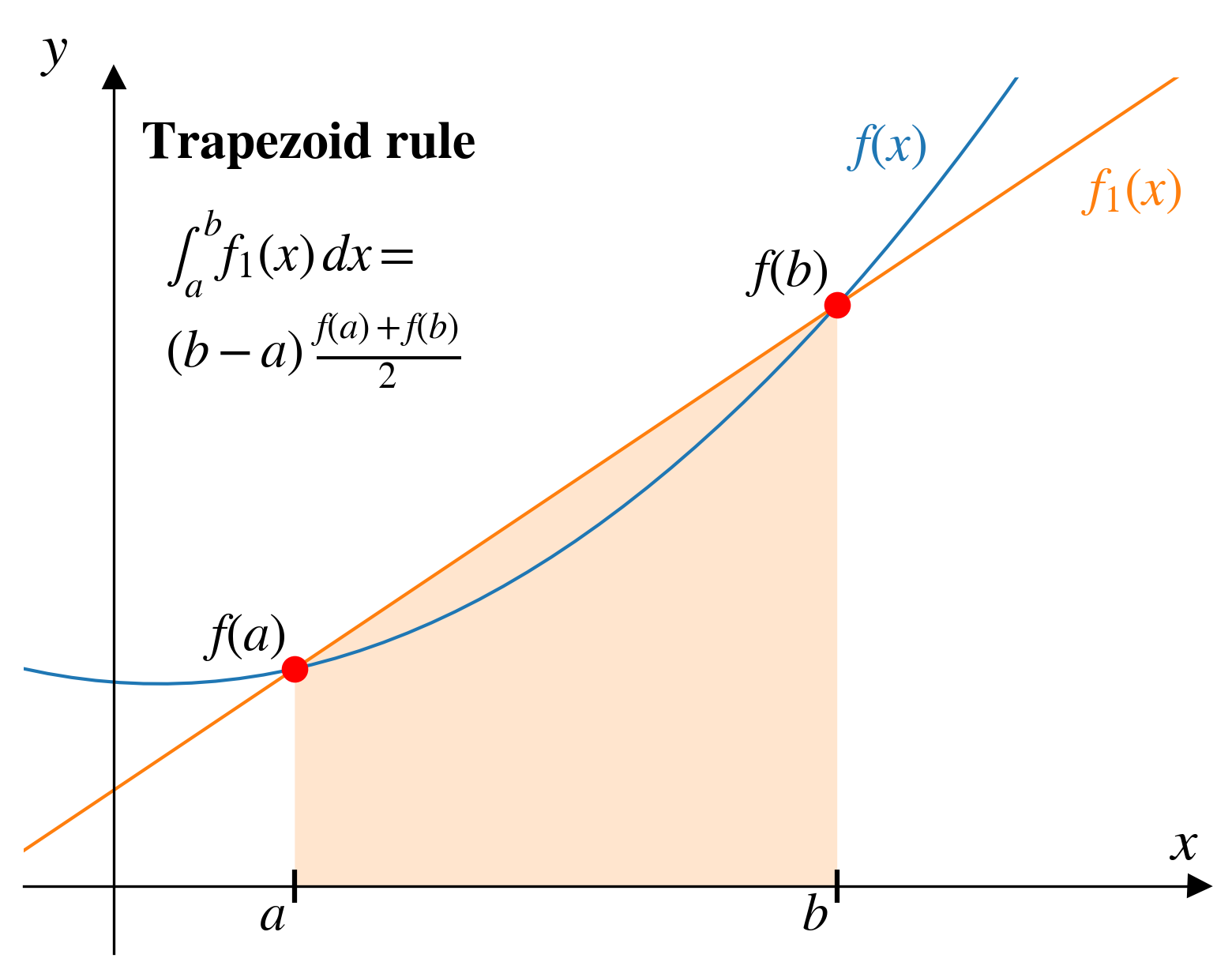
The integral of \(f_1(x)\) is simple to calculate:
\[\int_{a}^{b} f_1(x)\,dx = (b-a)\frac{f(a) + f(b)}{2}\]
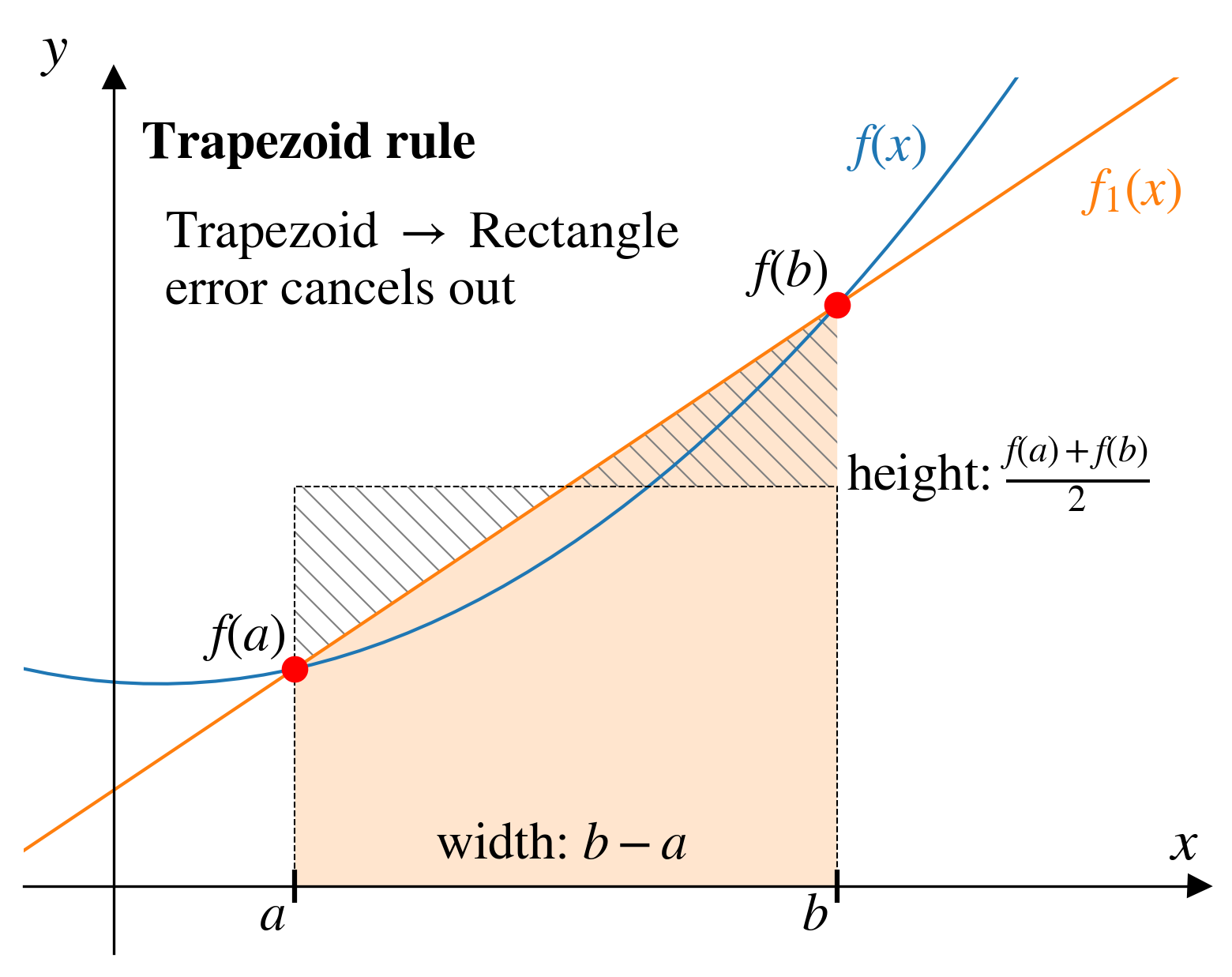
It’s composed of two parts:
- the width: \((b-a)\)
- the effective height: \(\displaystyle \frac{f(a) + f(b)}{2}\)
Trapezoid rule
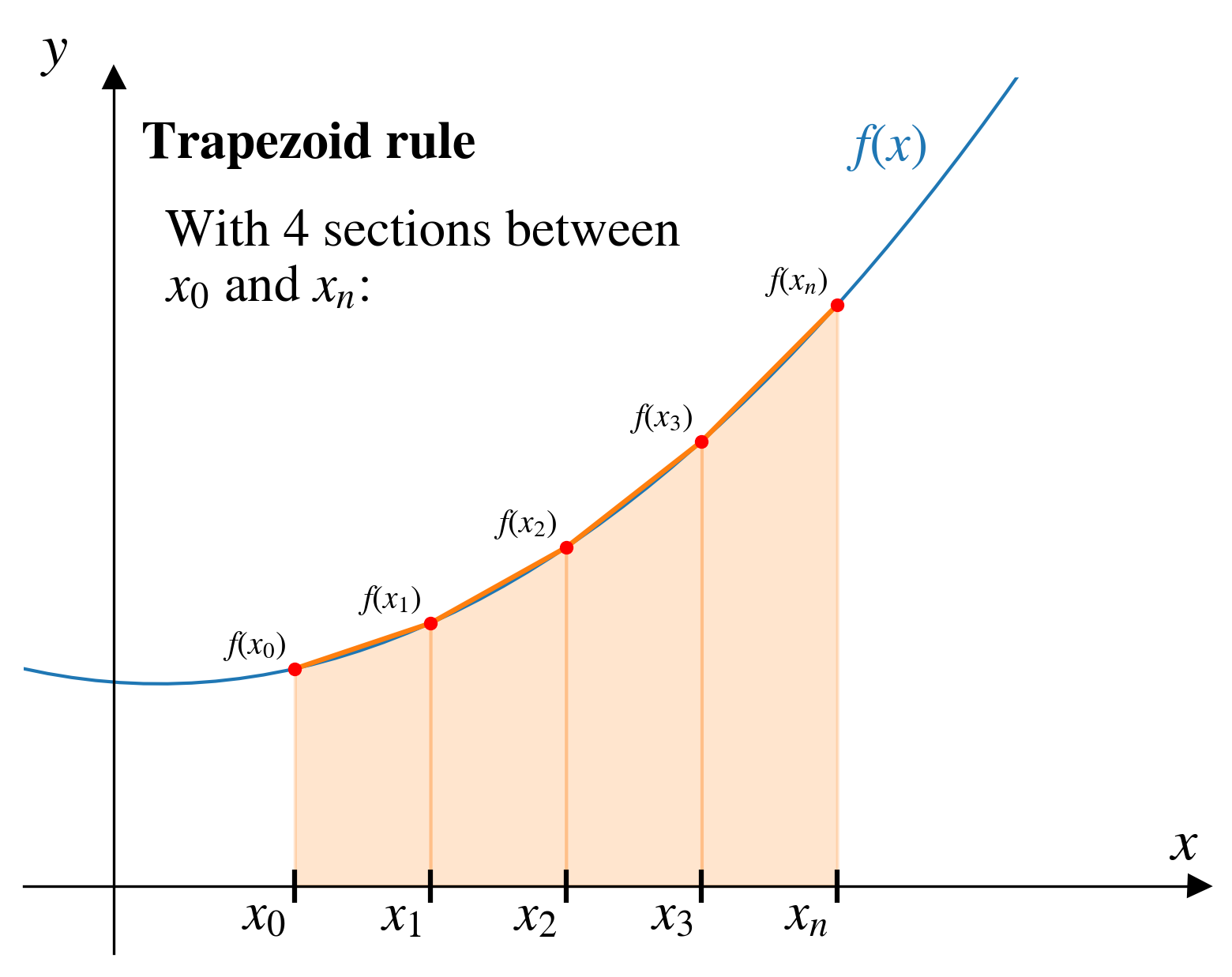
\(n-1\) again?
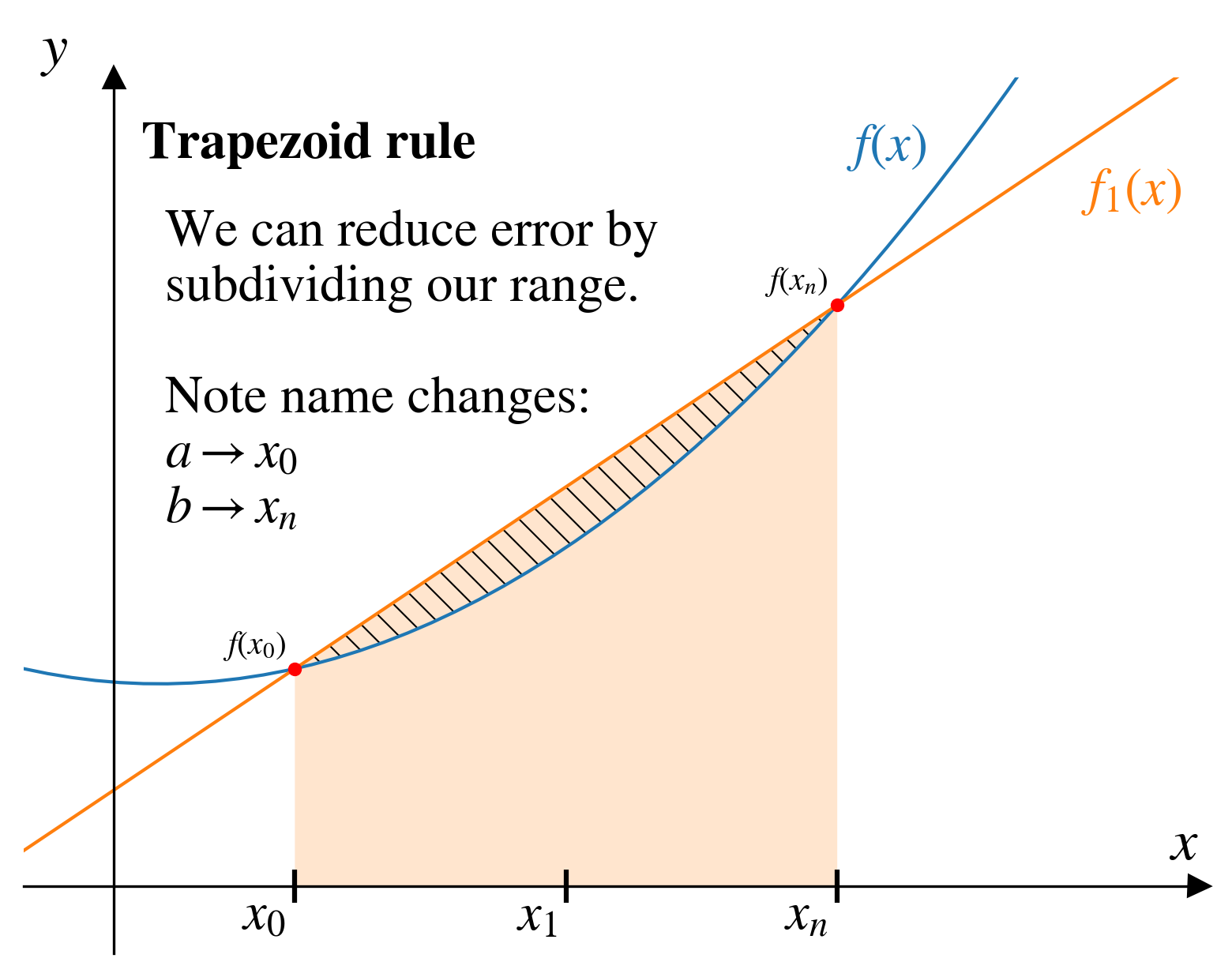
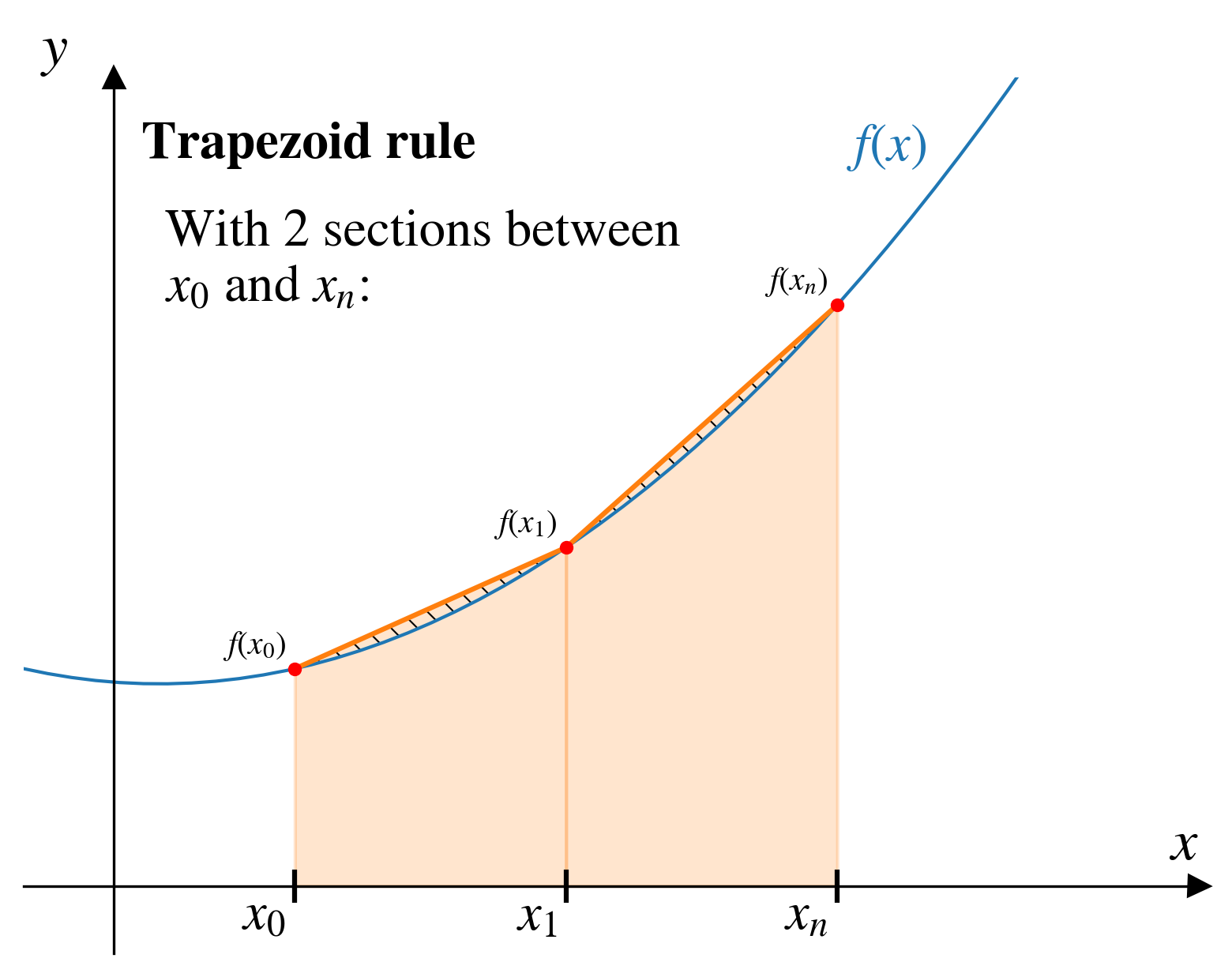
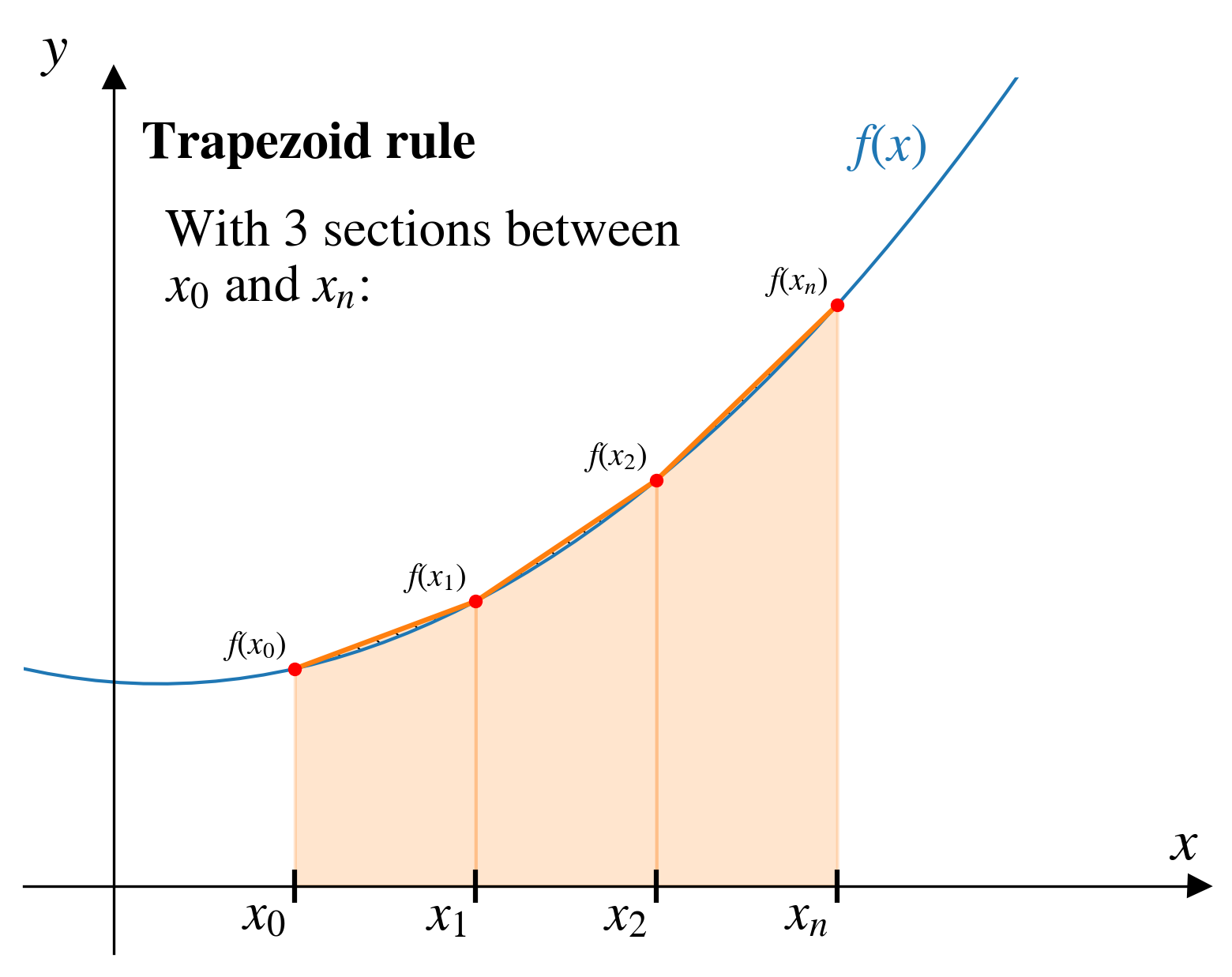
With \(n\) points, our approximate integral gives us \(n-1\) trapezoids…
Think of each trapezoid as areas corresponding to \(x_1\) through \(x_n\).
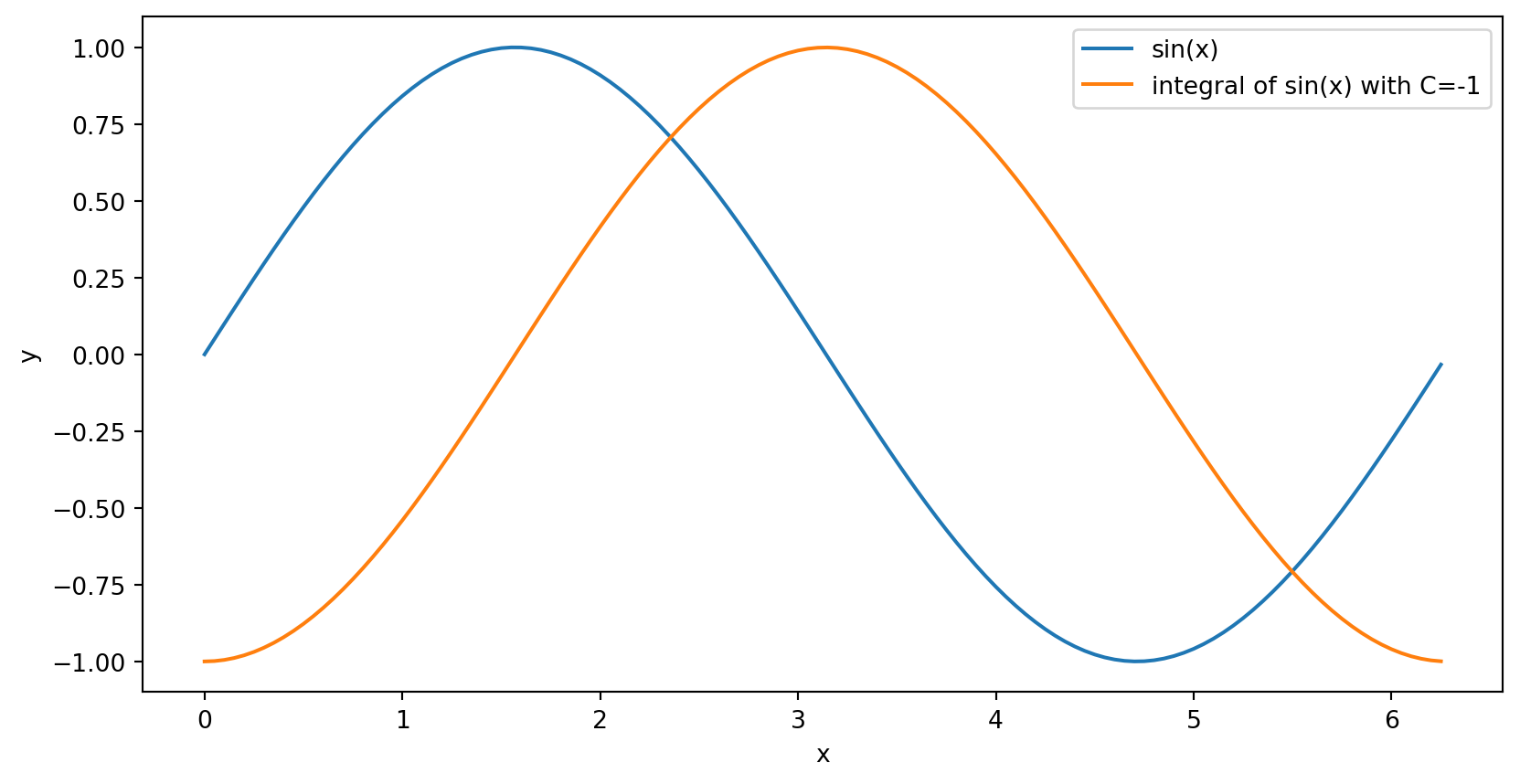
If we want \(n\) points for our integral, assign \(x_0 = 0\) and then add the integration constant, \(C\) to the entire integral array
Numerical integration in Scipy
Scipy has a function for discrete integration: scipy.integrate.cumulative_trapezoid
Length of x: 126
Length of y: 126
Length of I: 125Numerical integration in Scipy
Scipy has a function for discrete integration: scipy.integrate.cumulative_trapezoid
The length of x, y, and I:
Length of x: 126
Length of y: 126
Length of I: 126Numerical integration in Scipy
Scipy has a function for discrete integration: scipy.integrate.cumulative_trapezoid
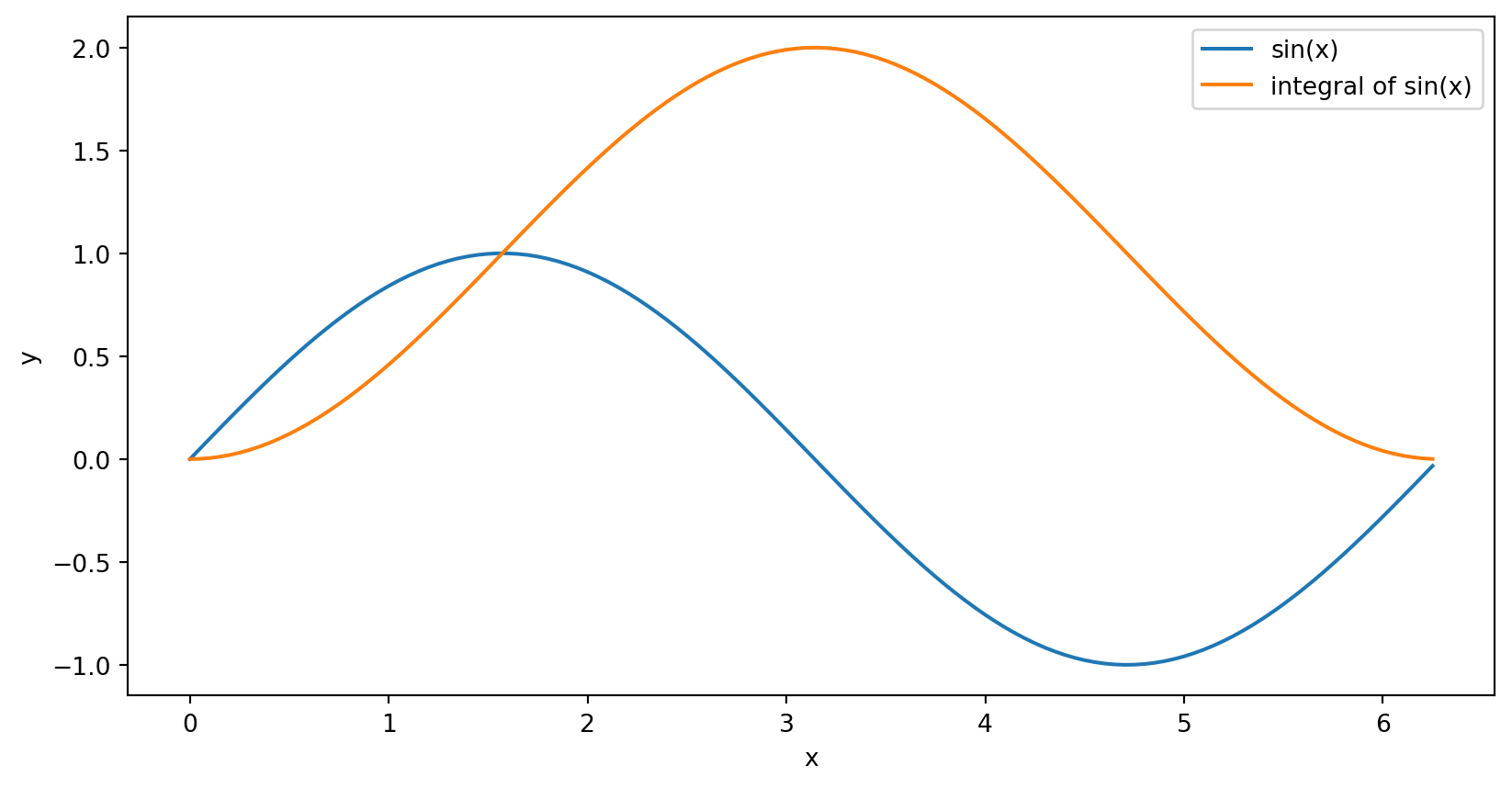
Numerical integration in Scipy
Scipy has a function for discrete integration: scipy.integrate.cumulative_trapezoid