TME 310 - Computational Physical Modeling
Root-finding
Lorne Arnold, PhD, PE
University of Washington Tacoma
Roots of equations
A root of an equation is a value of the independent variable that makes the equation equal to zero.
For example, the root of a linear equation with the form
\[ y = mx + b\]
is
\[-\frac{b}{m}\]
Non-trivial root-finding
What about more complicated examples?
We have a few options:
- Graphical methods
- Bracketed methods
- Open methods
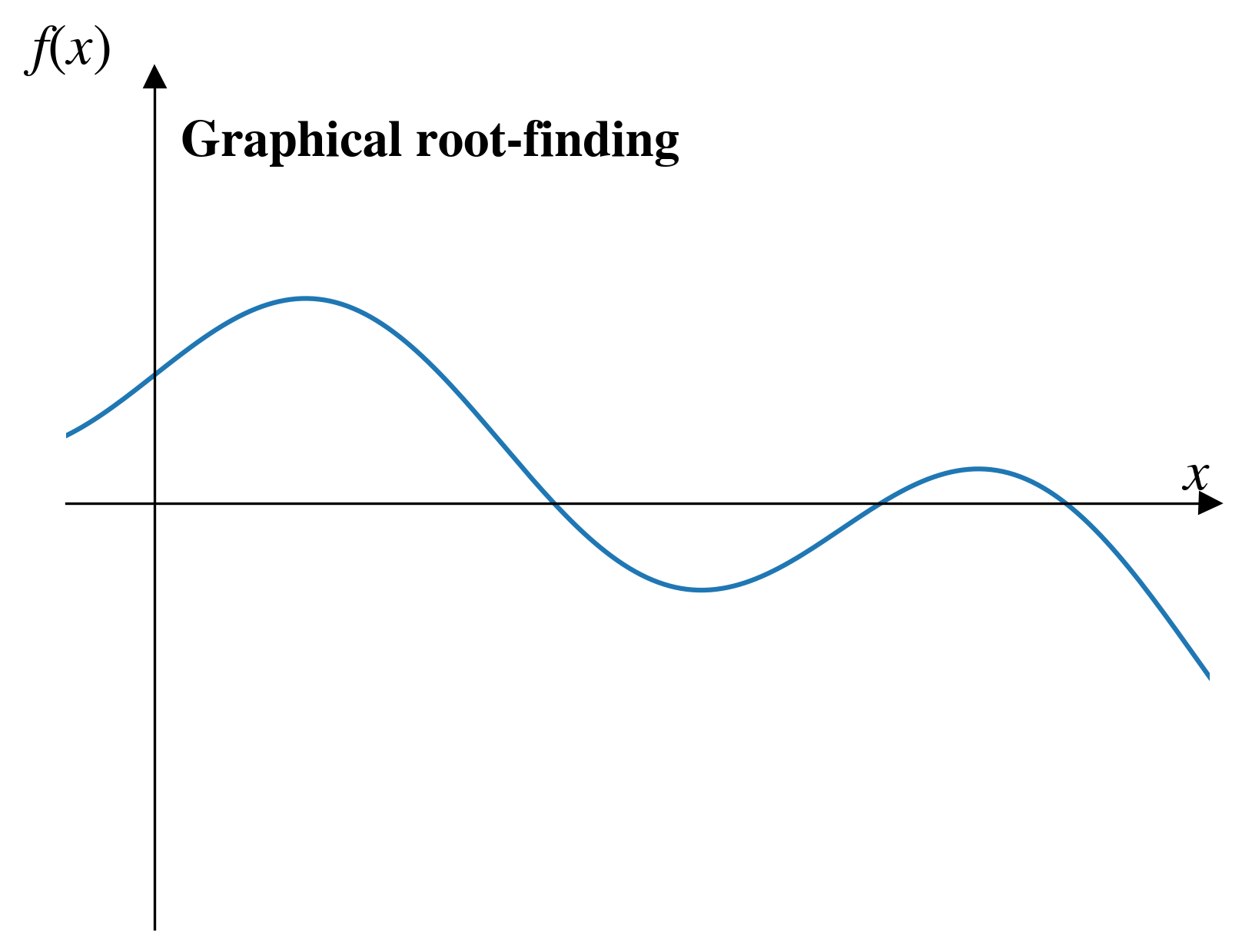
Graphical methods
A brute force solution:
- Plot the function
- Look for where it equals zero
Graphical method
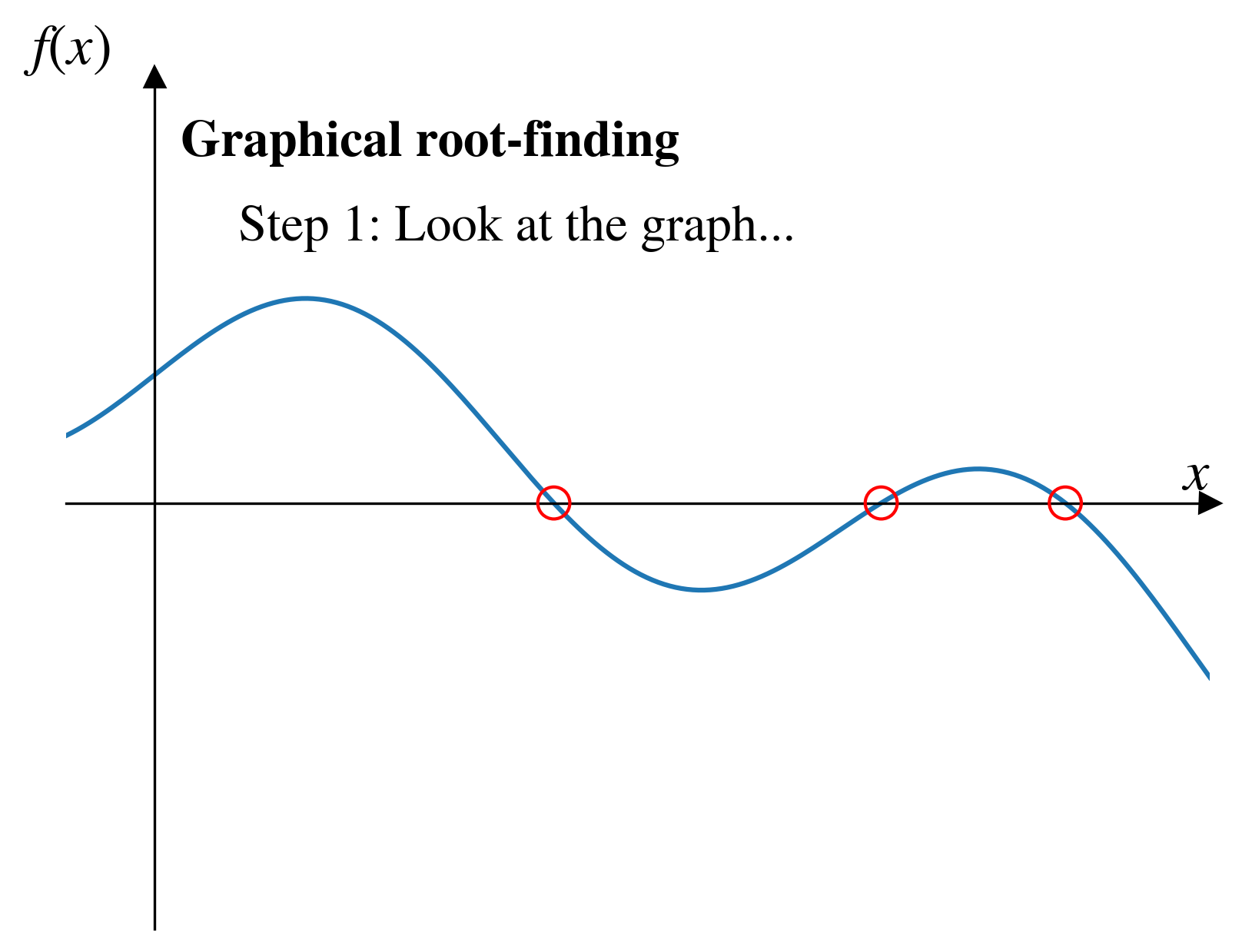
Pros and cons (graphical methods)
Pros
- Reliable
Cons
- Slow
- Imprecise
Graphical methods are a great check for faster, automated methods.