TME 310 - Computational Physical Modeling
Open methods (root-finding)
Lorne Arnold, PhD, PE
University of Washington Tacoma
Root-finding methods
We have a few options:
- Graphical methods
- Bracketed methods
- Open methods
- Newton-Raphson
- Secant method
Open methods
Algorithms for searching from a single starting point
- Newton-Raphson:
- Choose a starting point.
- Look for the root where a line tangent (i.e., local derivative) to the function intersects horizontal axis.
- Repeat until tolerance is satisfied.
- Secant method
- Same thing, but with a secant line from an approximate derivative.
Newton-Raphson
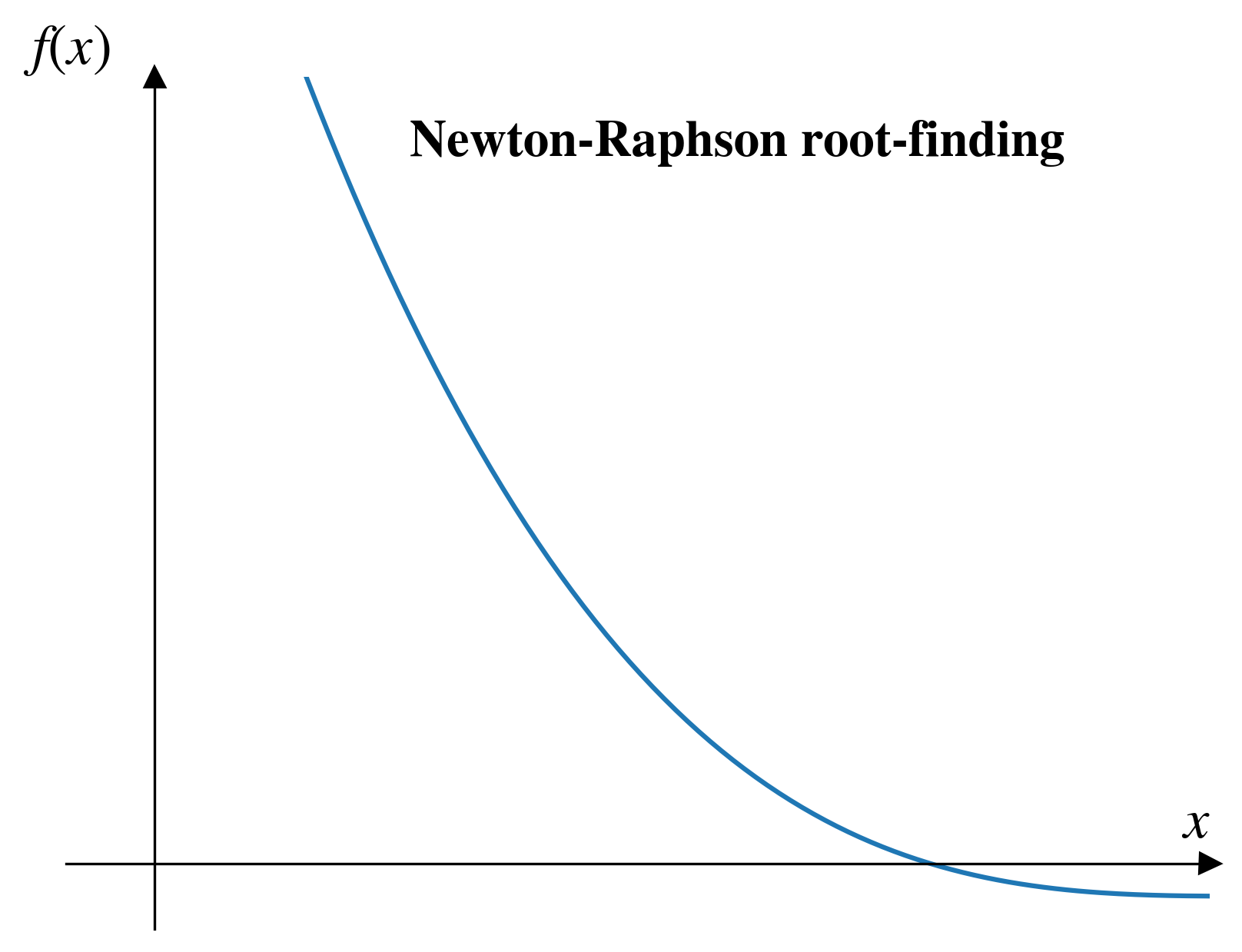
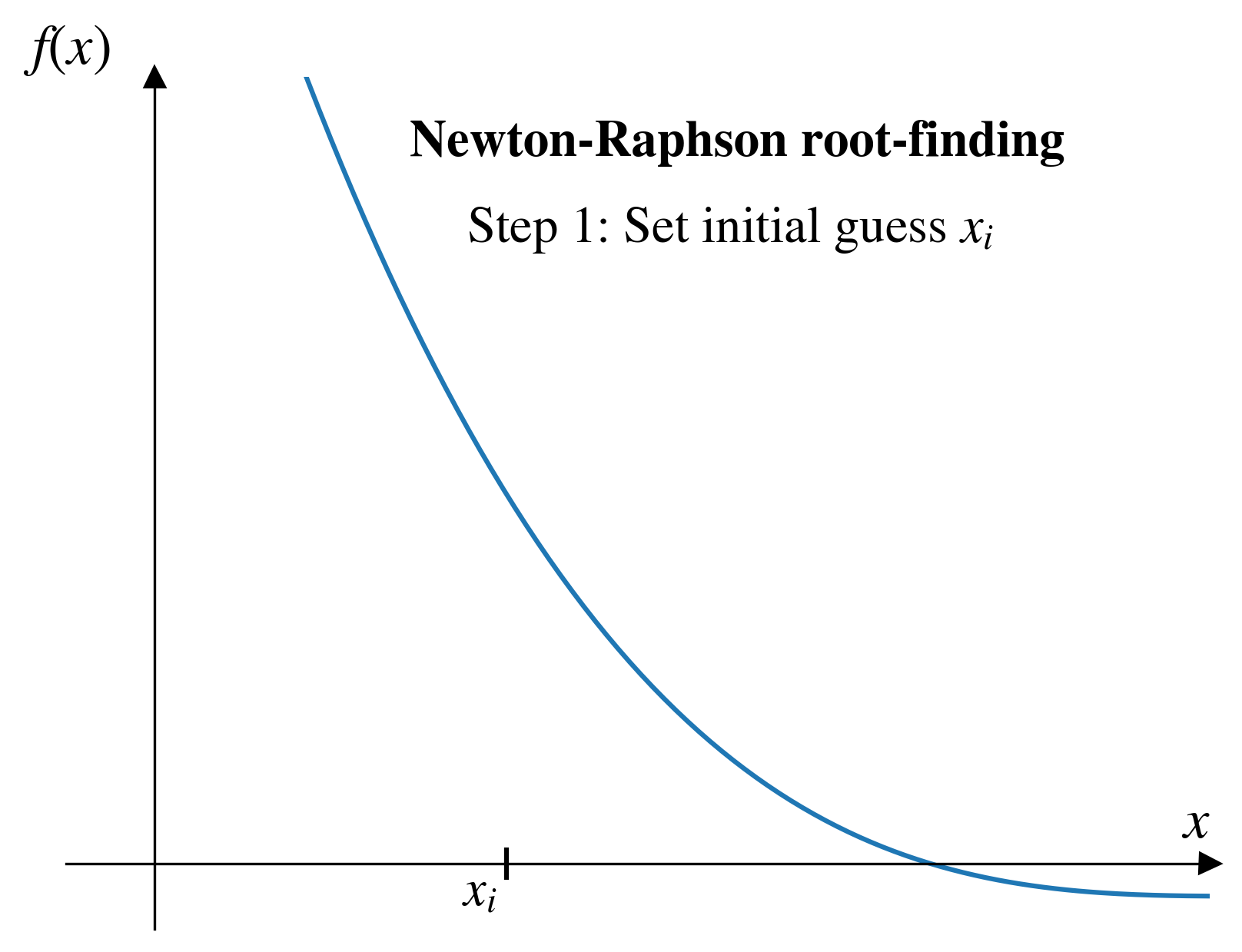
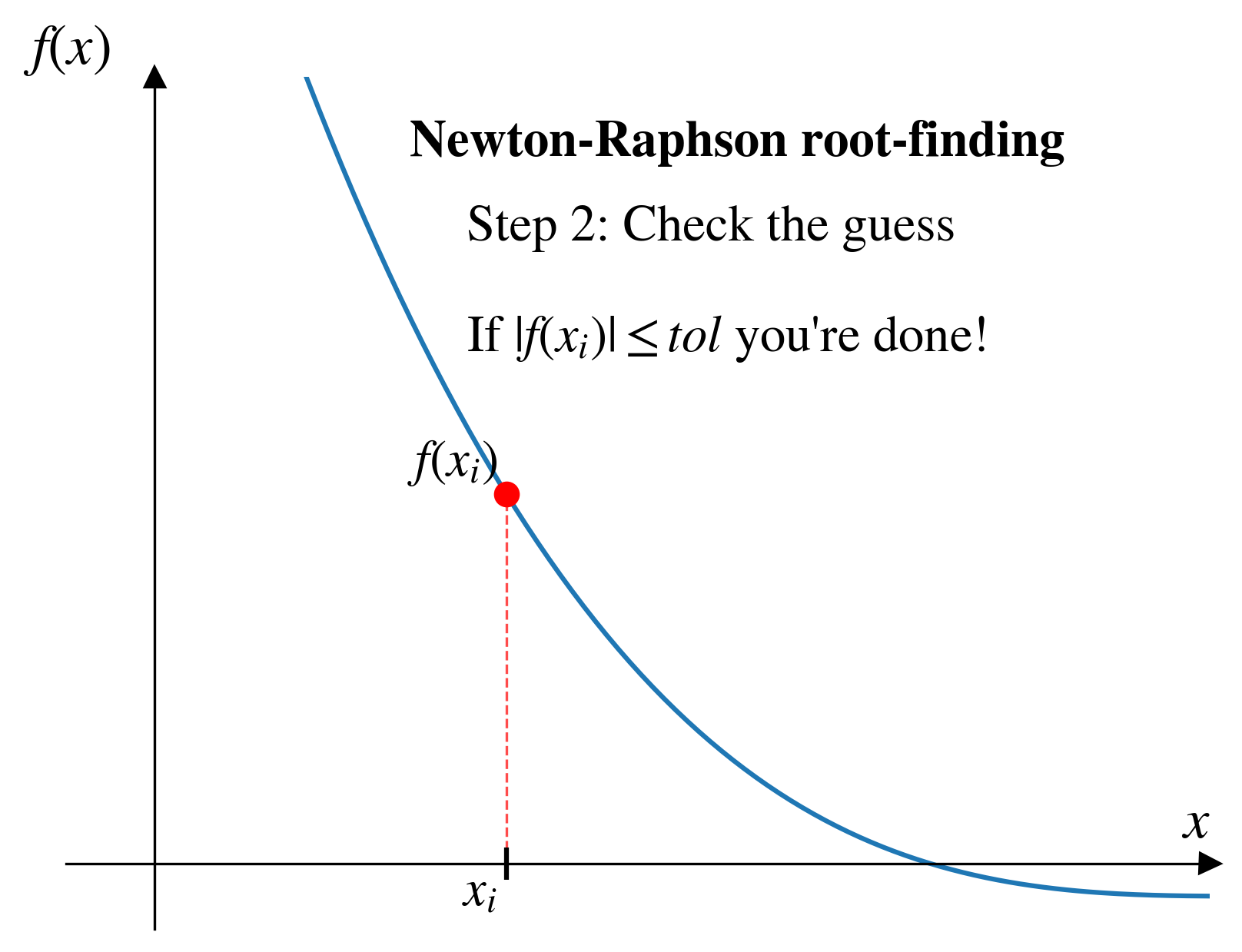
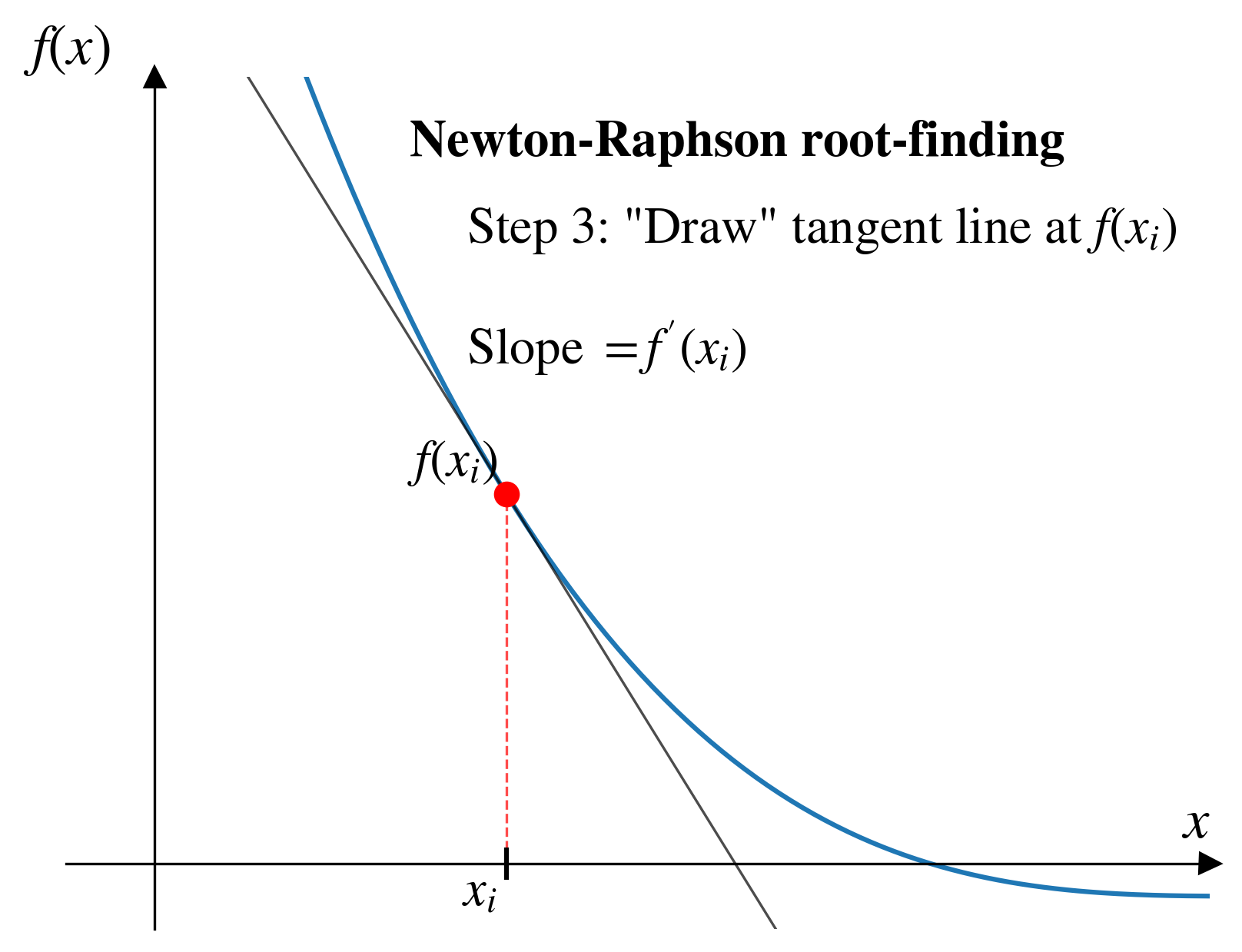
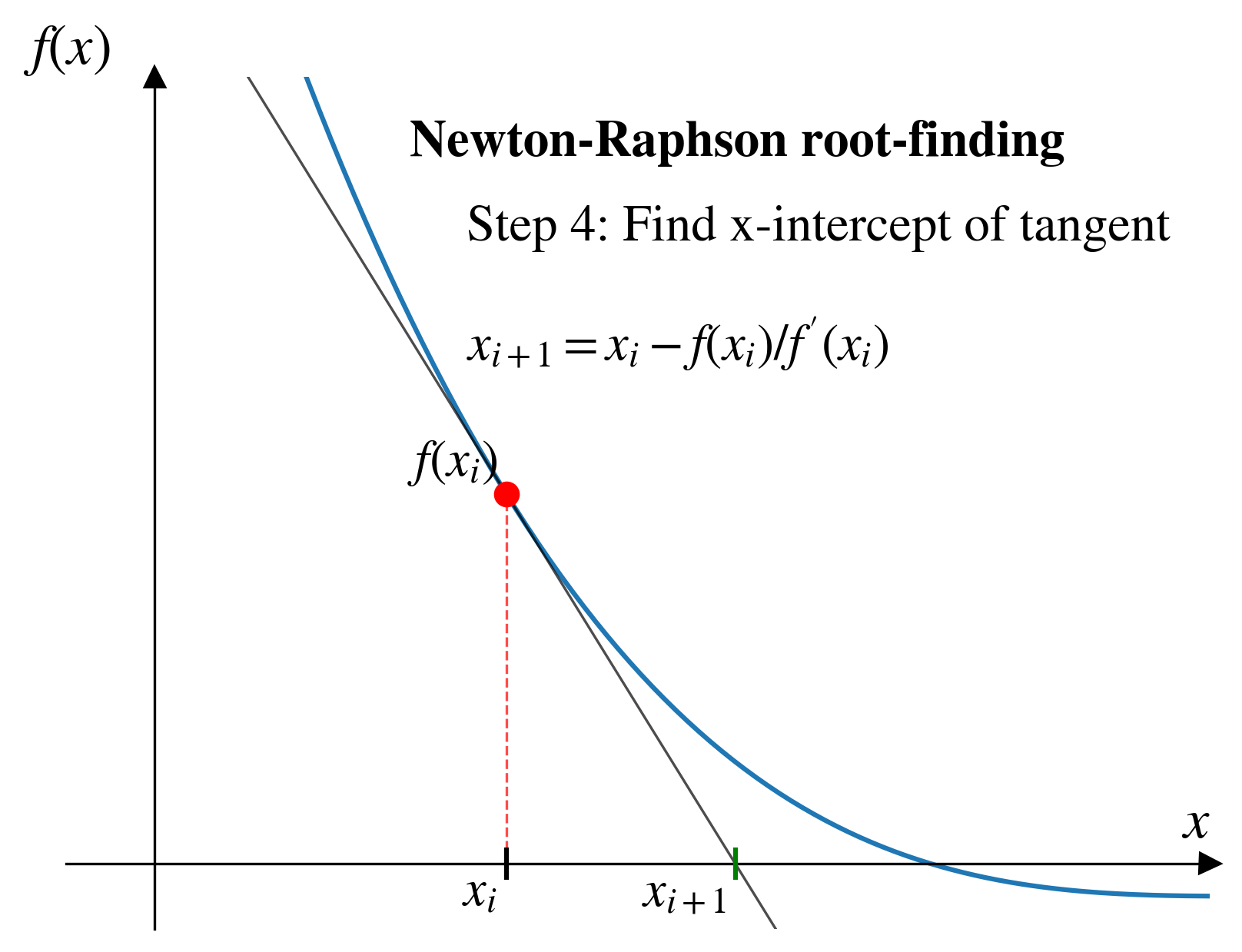
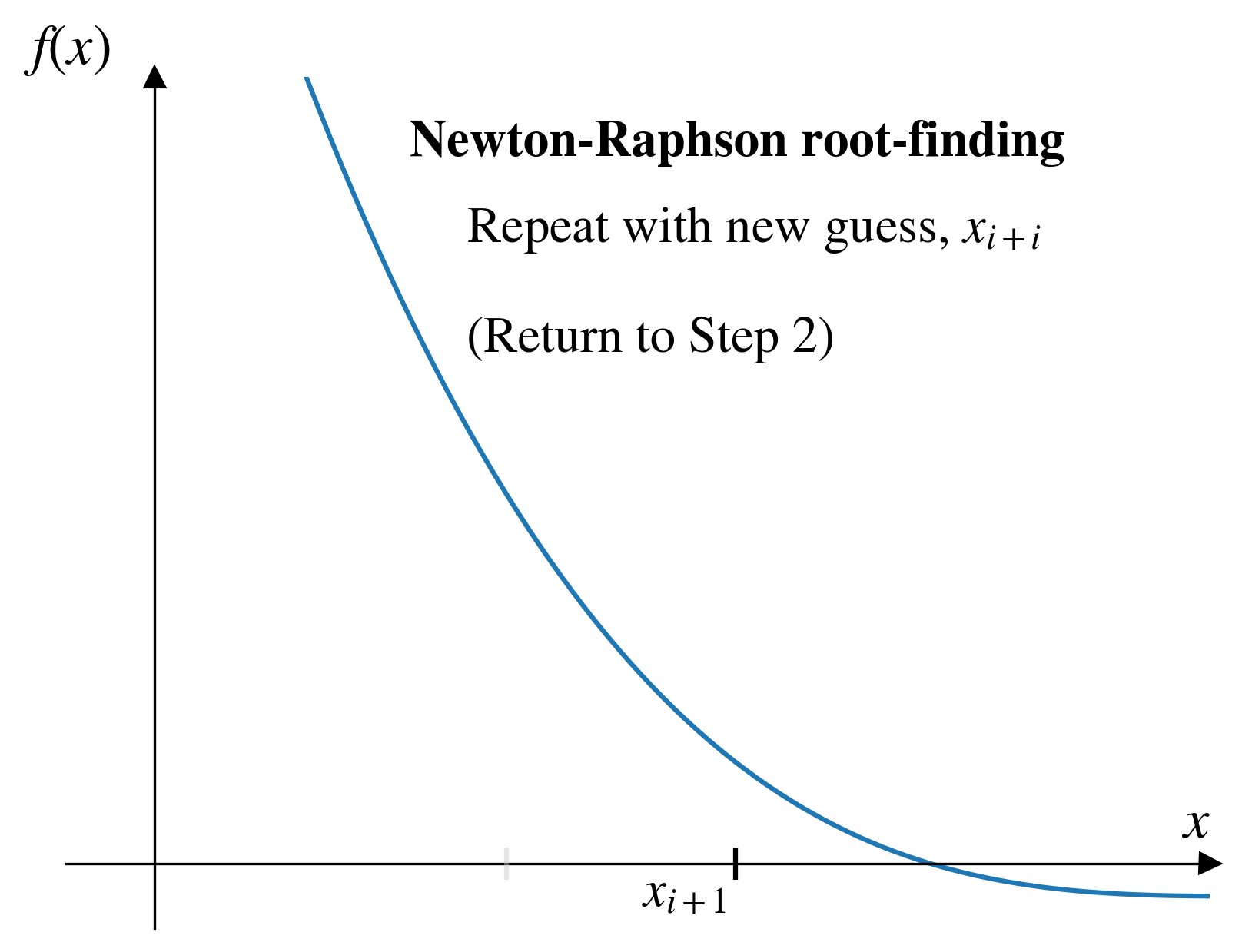
Pros and cons (Newton-Raphson)
Pros
- Fast convergence (faster than bisection)
- Simple
- Unbounded
Cons
- Need to know the derivative!
- Can’t start where derivative is zero
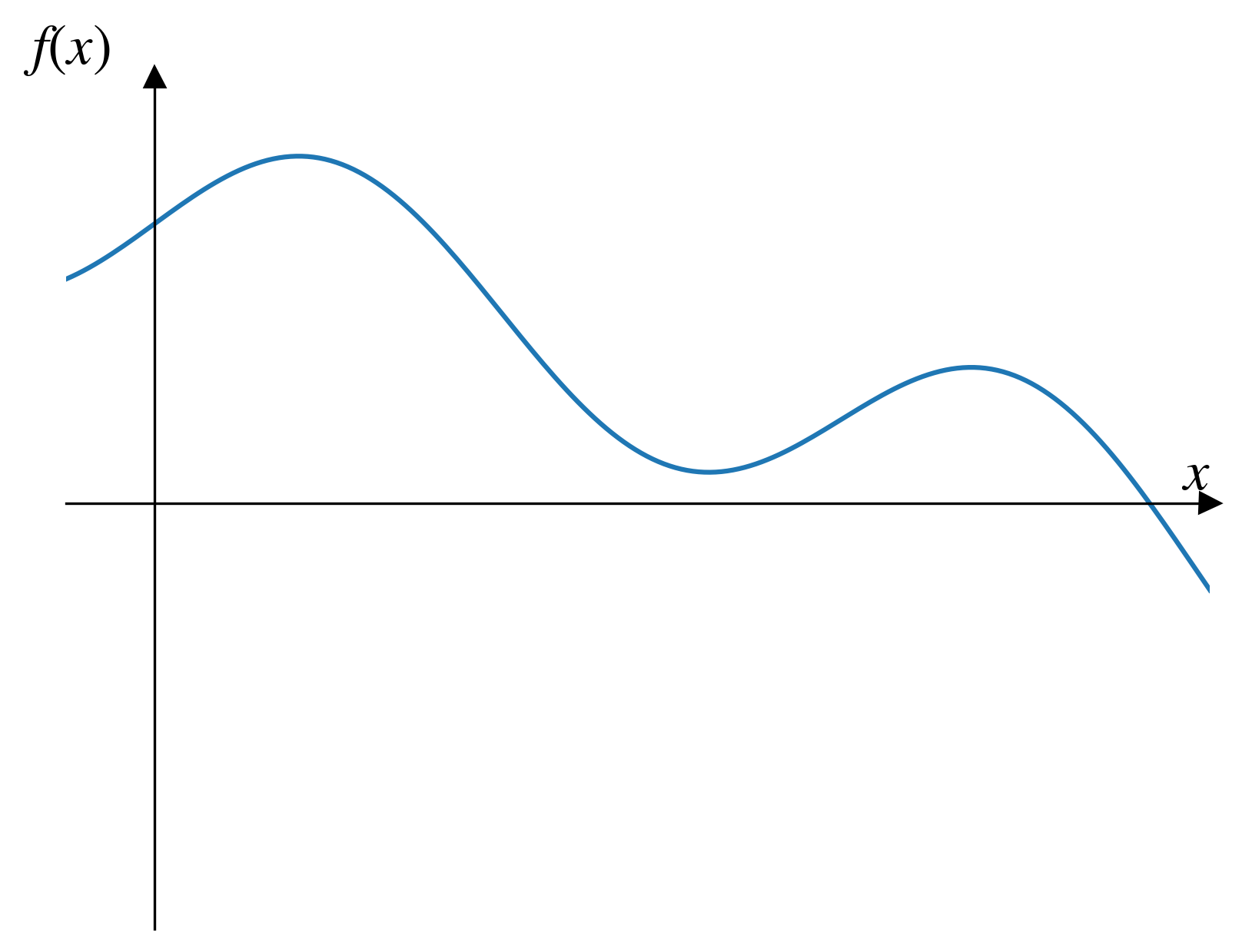
- It can get caught in a local maximum/minimum
Local maxima/minima problem
Secant method
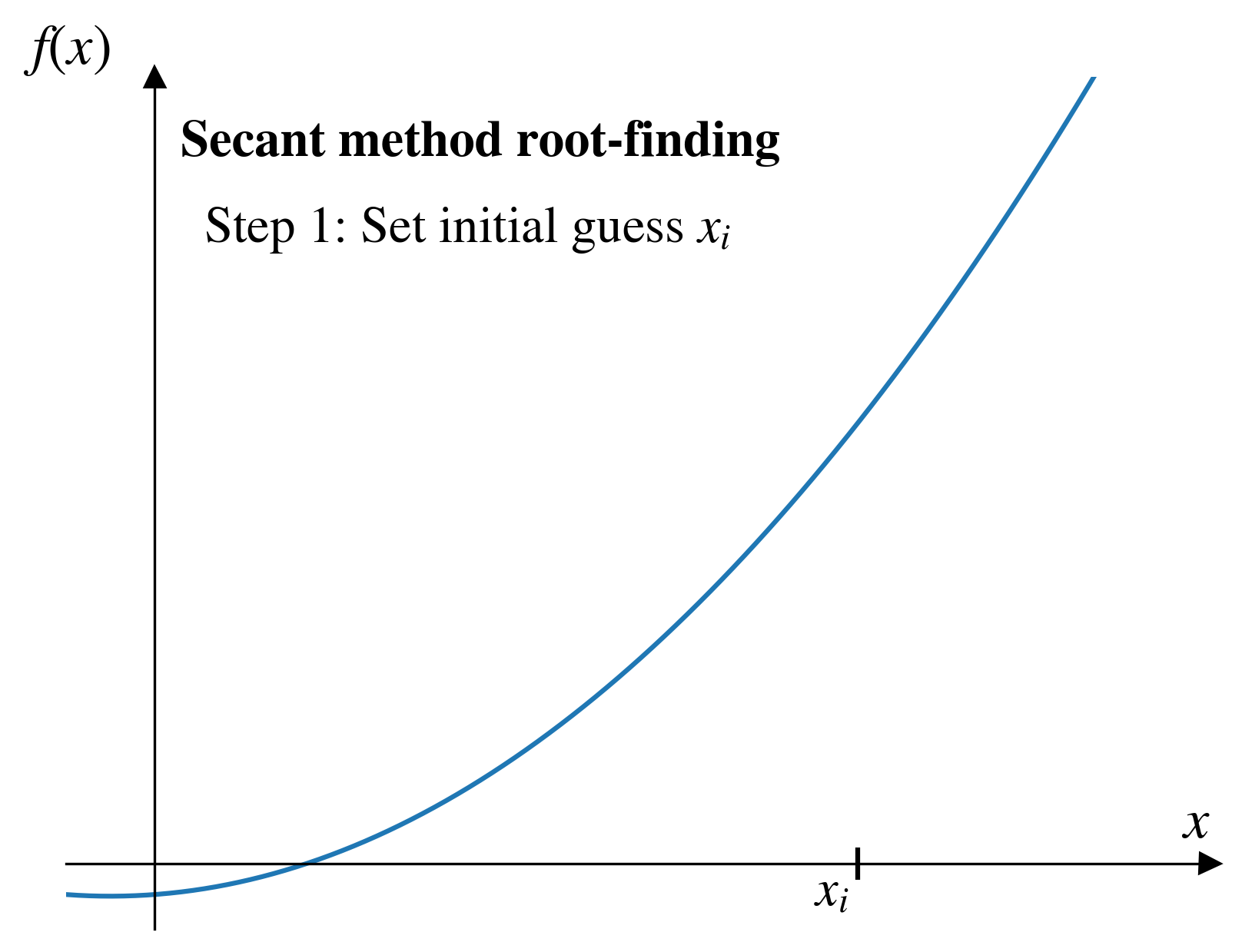
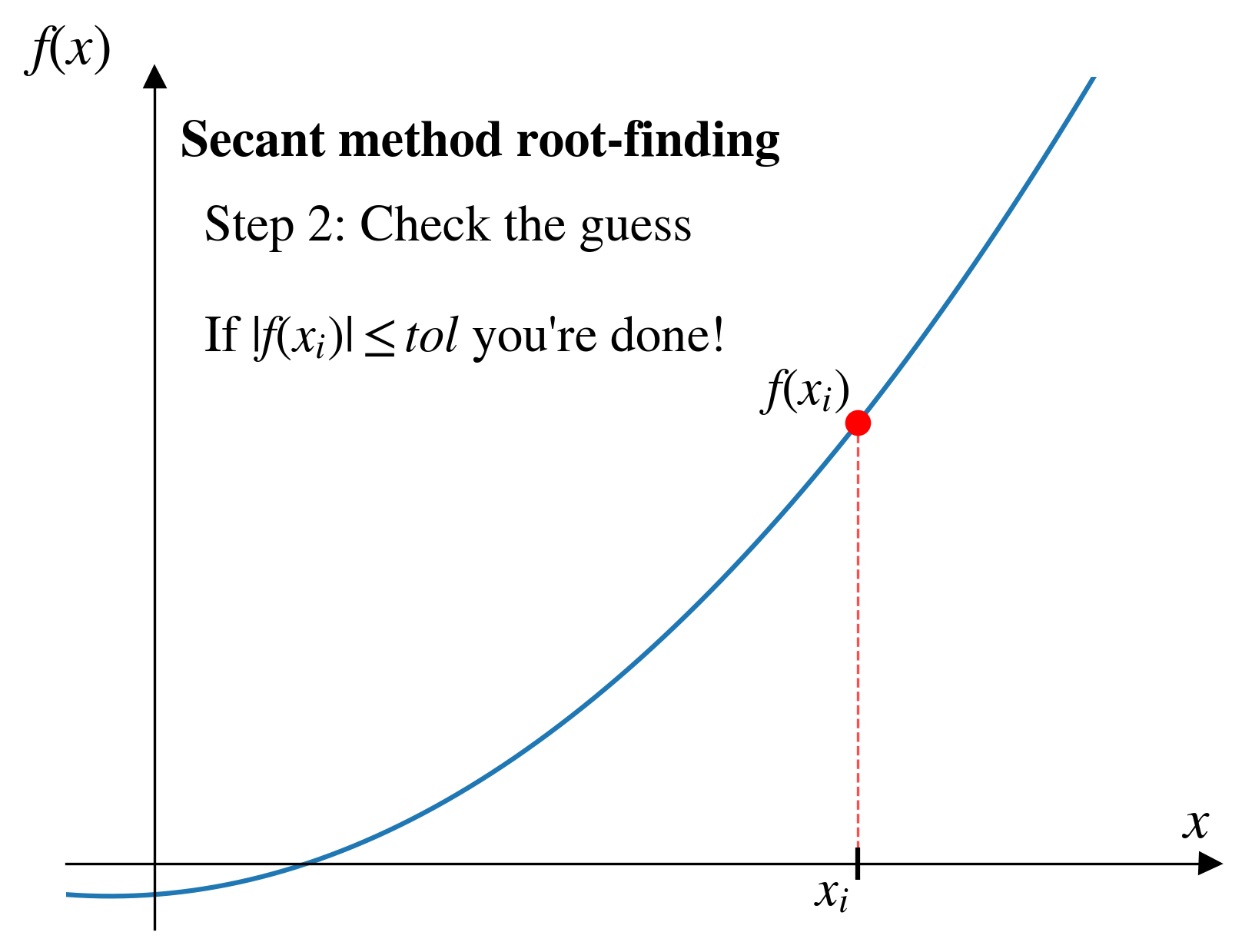
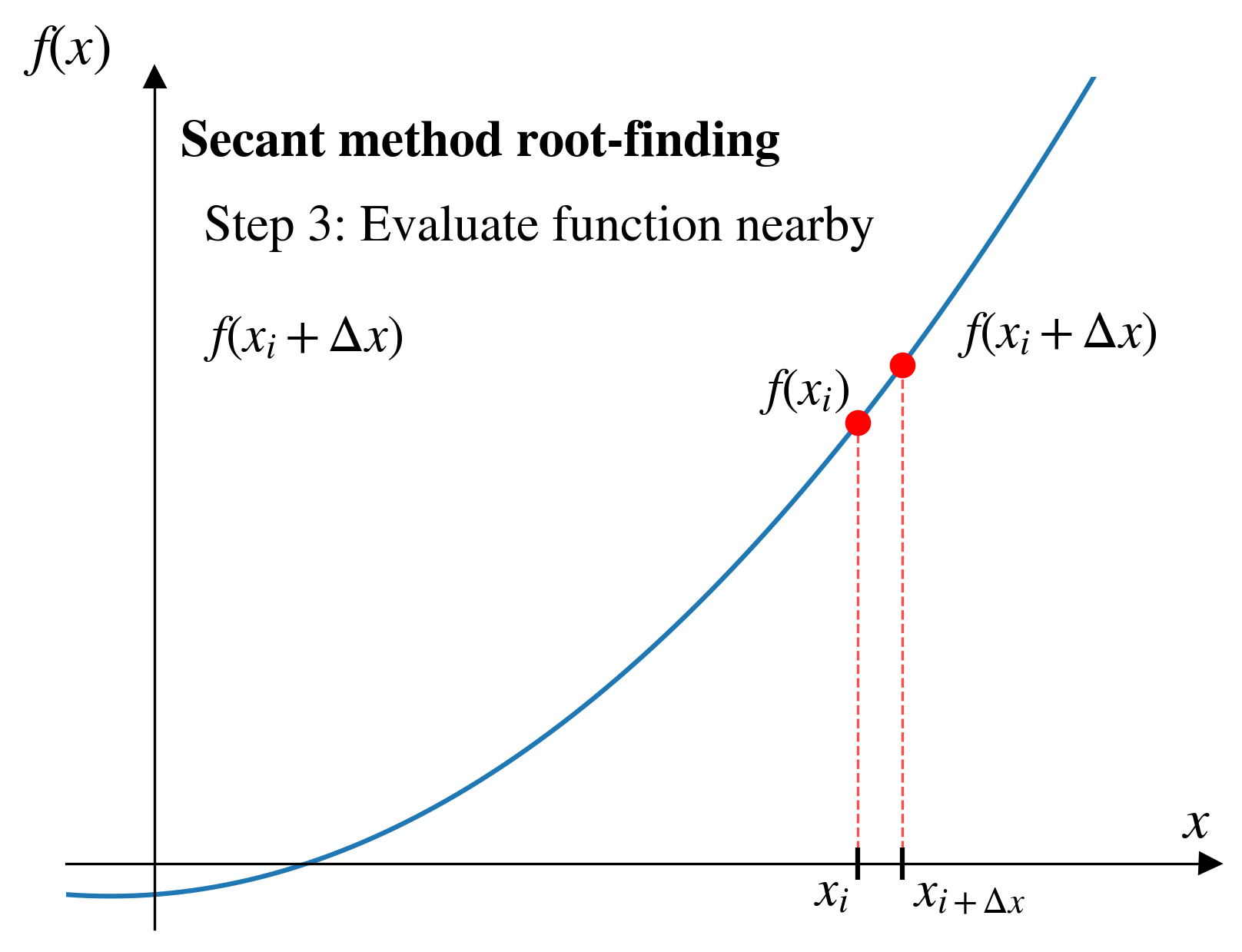
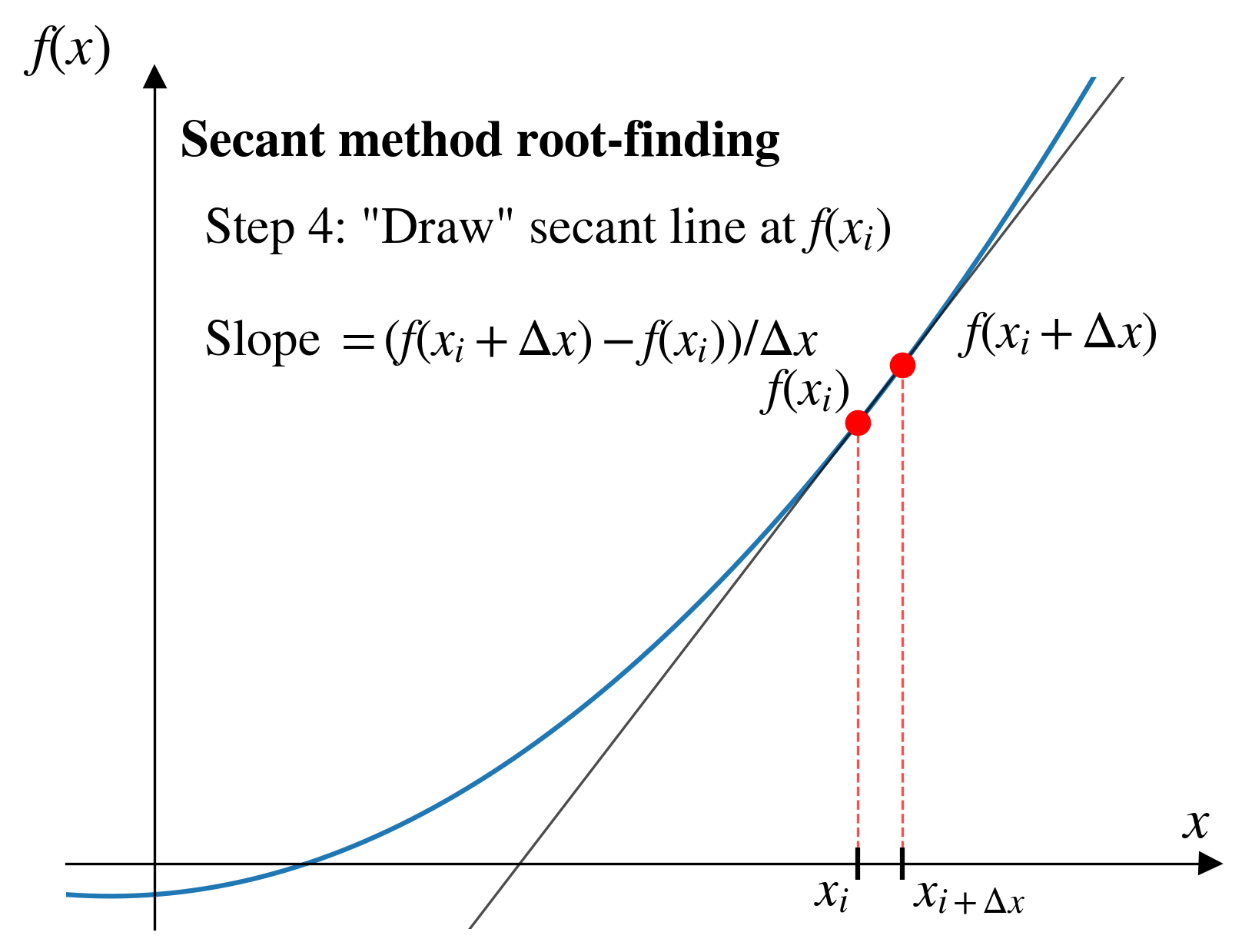
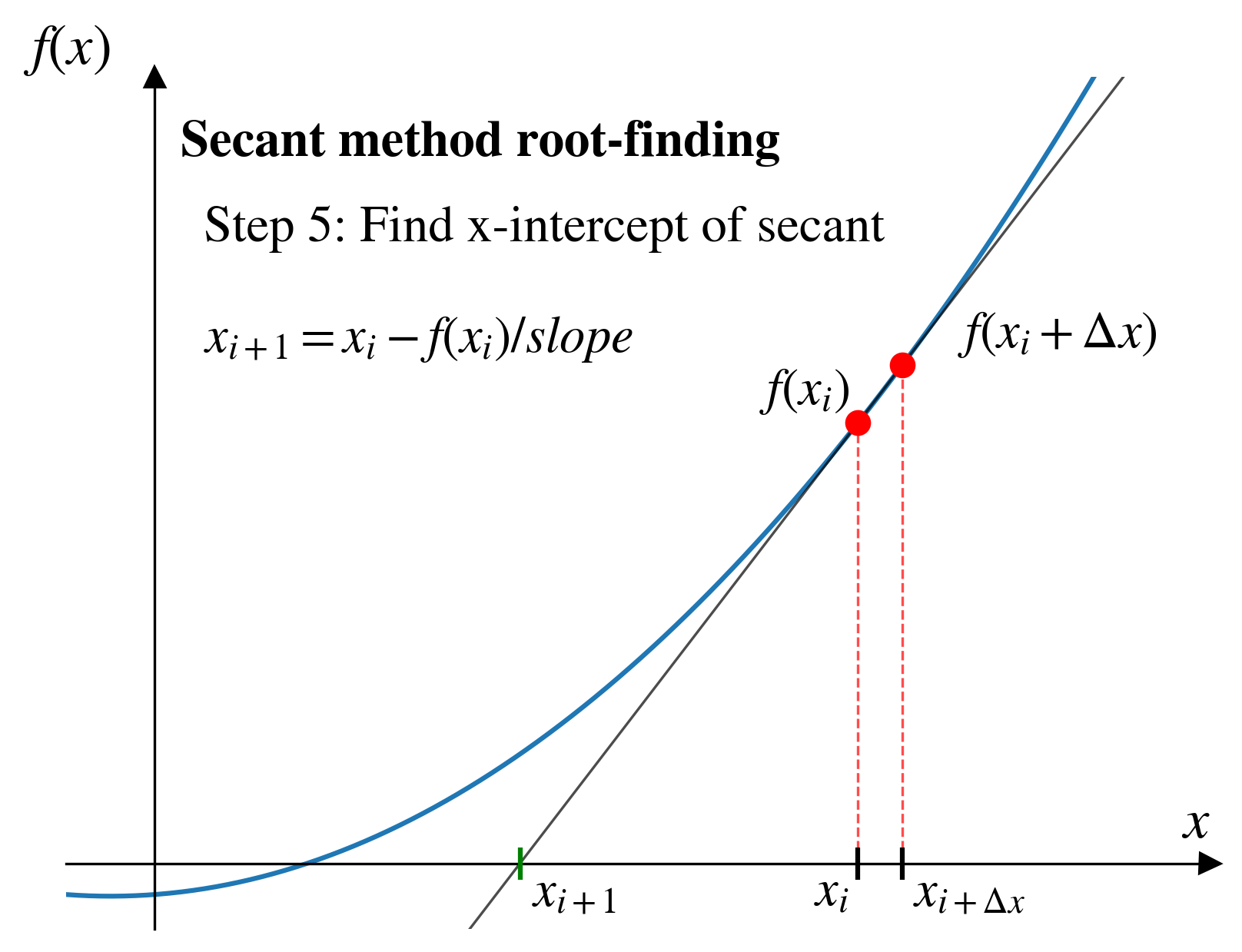
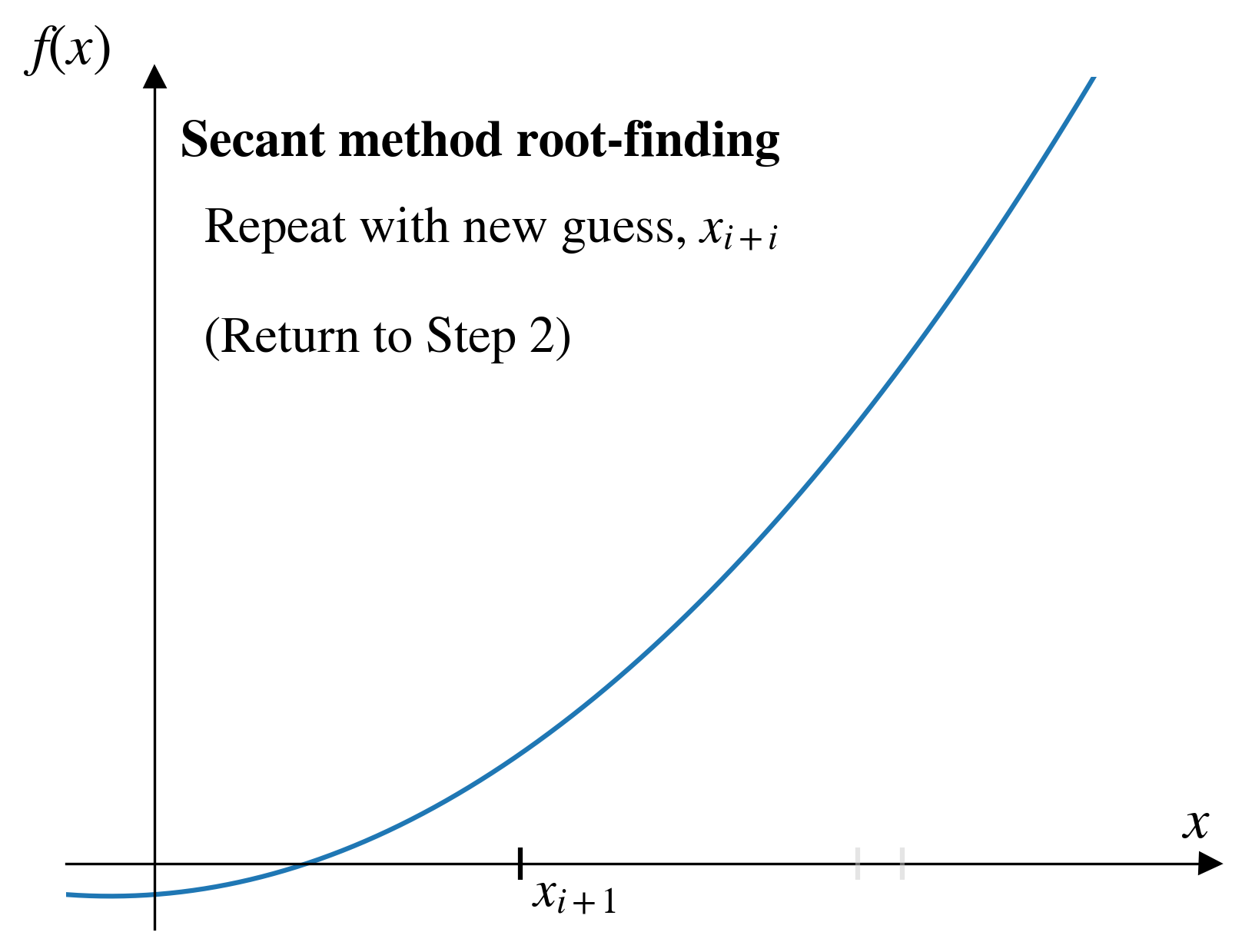
Pros and cons (secant)
Pros
- Same as Newton-Raphson, plus…
- Don’t need to know the derivative
- Less strict about starting points
Cons
- It can get caught in a local maximum/minimum
Secant method is great if local maxima/minima are not a concern