num = 250.0; guess = 100.0 # find cubed root of "num" with initial "guess"
tol = 1e-2
e_a = 1
while abs(e_a) > tol:
new_guess = (2 * guess + num / guess**2) / 3 # some approx. method
e_a = (new_guess - guess) / new_guess # Approx. relative error
guess = new_guess
print(f"The cubed root of {num} is about {guess}")Error tolerance
TME 310 - Computational Physical Modeling
Lorne Arnold, PhD, PE
University of Washington Tacoma
Acceptable error
We can calculate the approximate error of our calculations. Depending on what our goals are, we can set a threshold of acceptable error (a.k.a a tolerance).
For example:
Find the value of \(\pi\) with an approximate relative error tolerance of \(1e^{-4}\) using the dartboard method.
A tolerance to finding \(\sqrt[3]{250}\)
The cubed root of 250.0 is about 6.299605894866889Dartboard method
Randomly throw darts at a square with an inscribed circle and calculate the ratio of darts that land inside the circle to the total number of darts.
r
- \(A_{circle} = \pi r^2\)
- \(A_{square} = 4 \times r^2\)
- \(\displaystyle \pi = \frac{4 \times A_{circle}}{A_{square}} \approx \frac{4 \times \text{darts in circle}}{\text{total darts}}\)
Visualizing the dartboard method
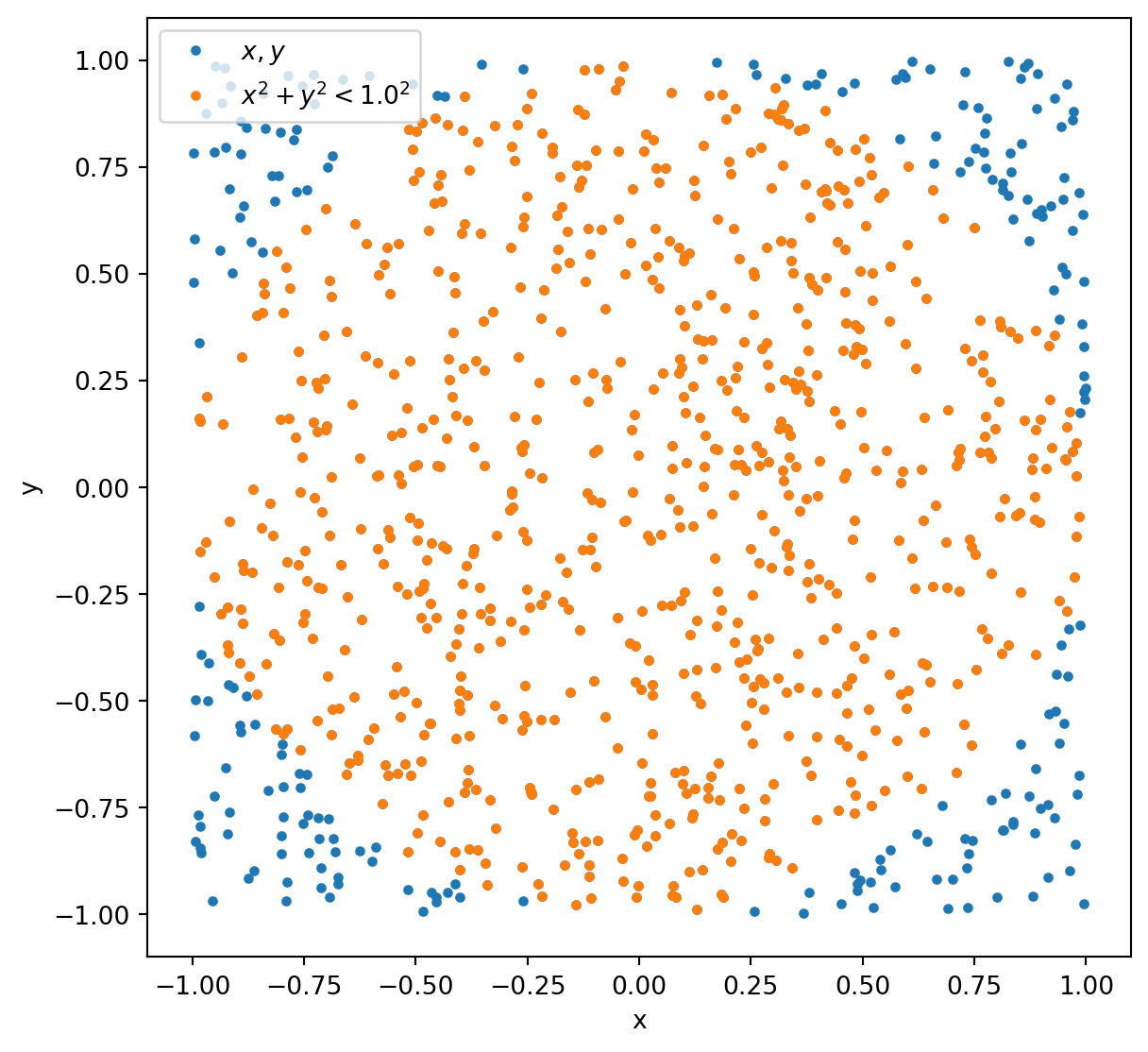
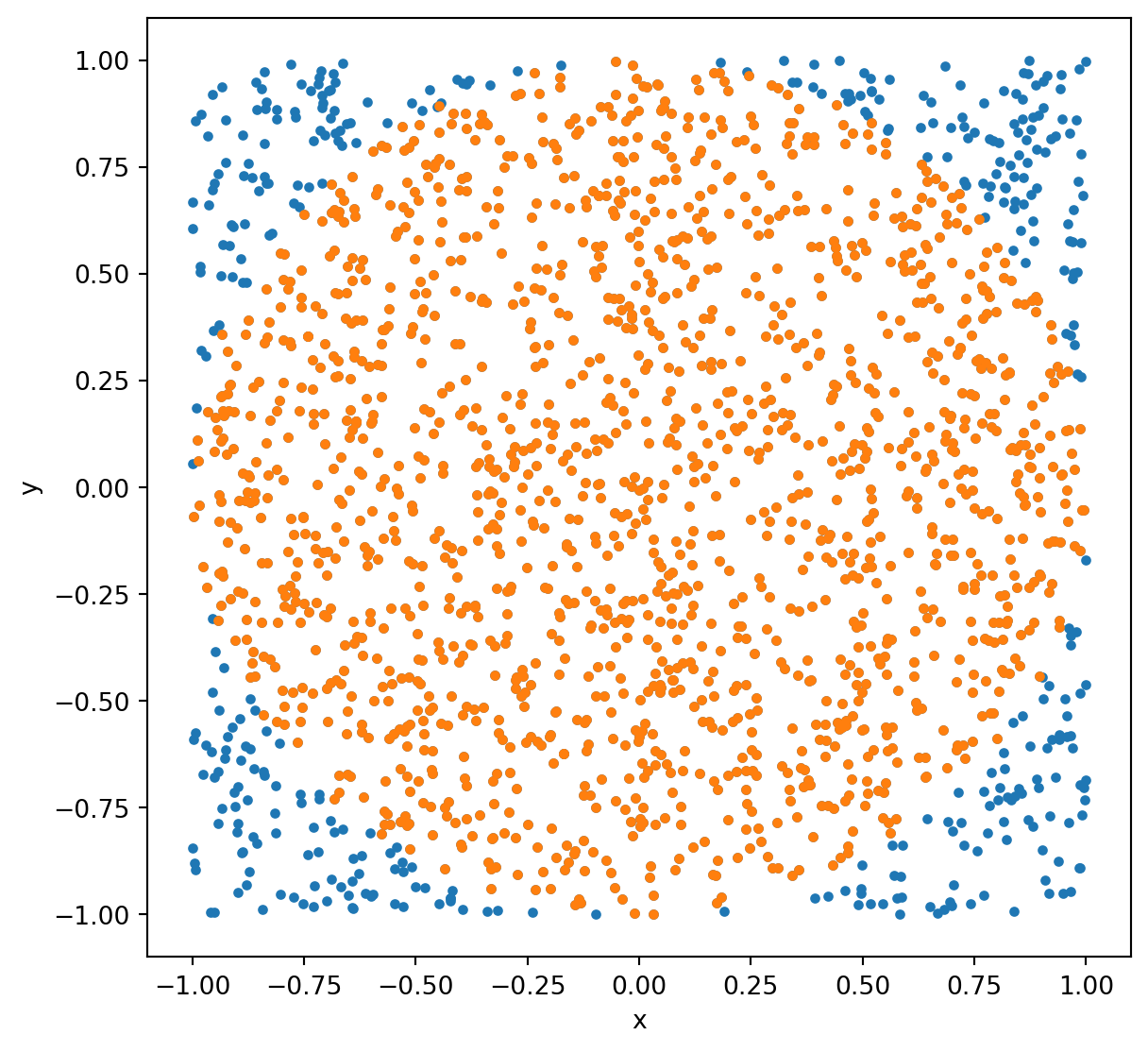
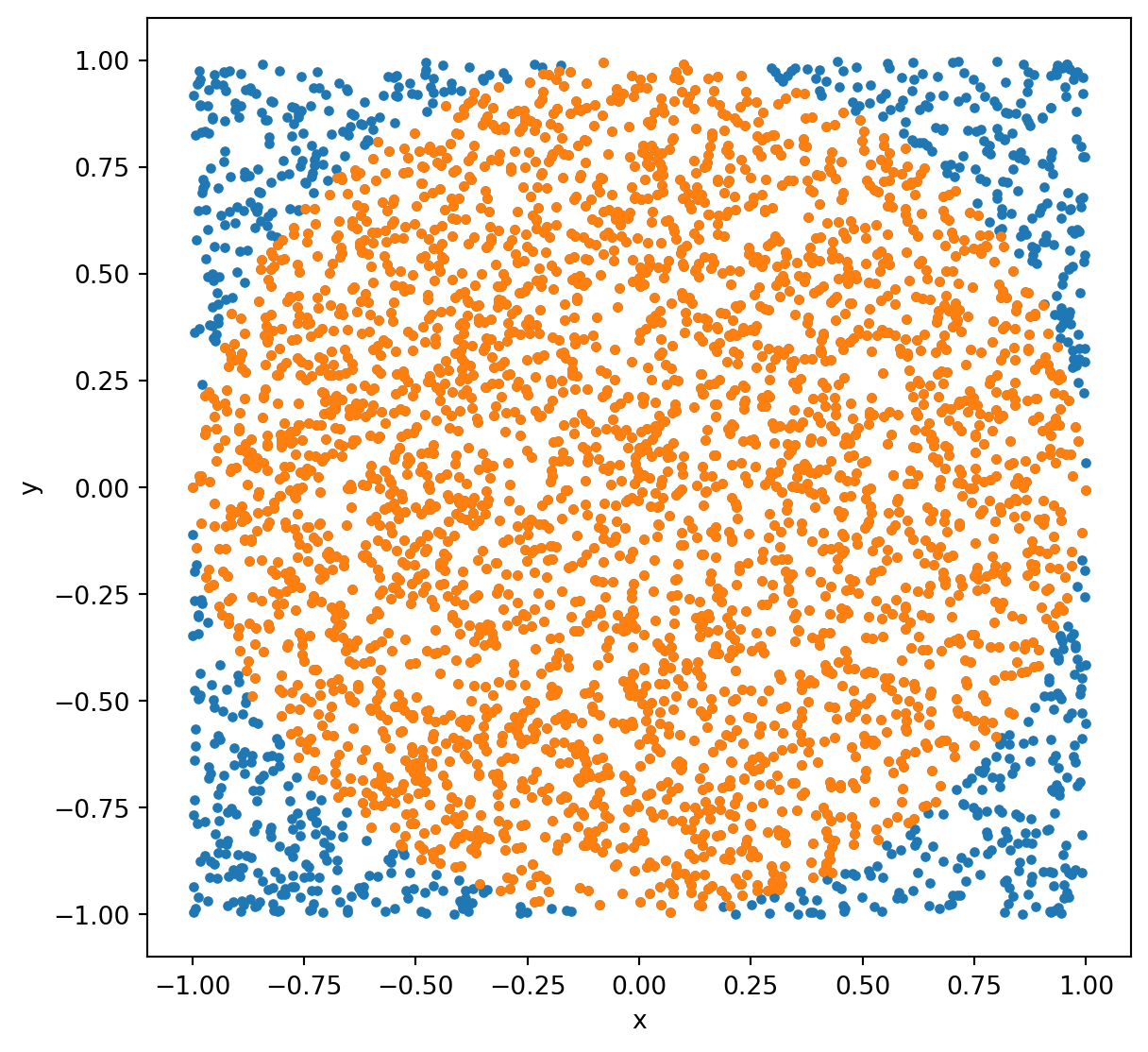
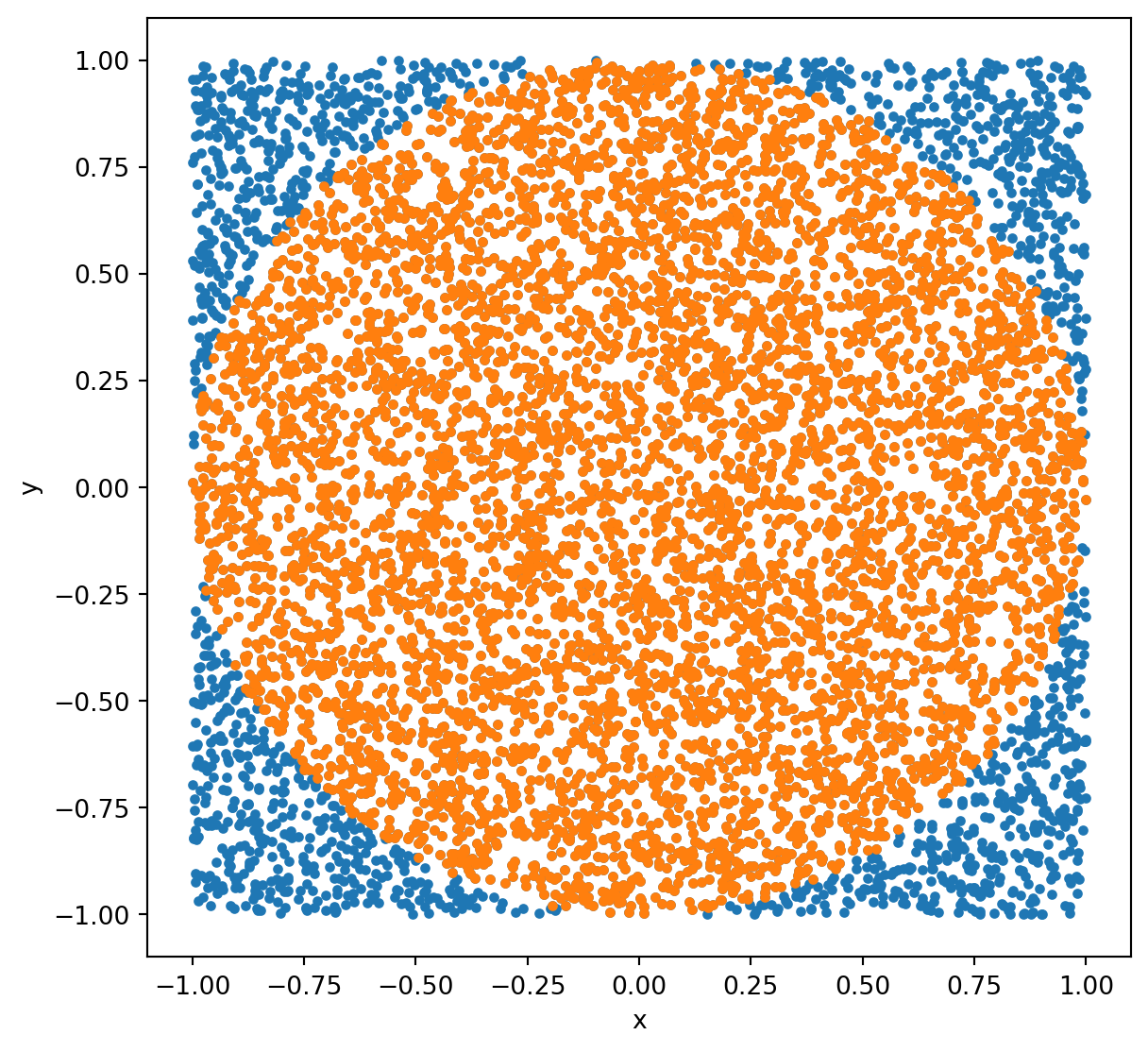
Challenge:
Use the dartboard method to approximate the value of \(\pi\). Continue “throwing darts” until your approximate relative error is less than 1e-4.