Array logic
TME 310 - Computational Physical Modeling
University of Washington Tacoma
Logical expressions
We have already seen logical expressions in places like while loops:
Logical expressions evaluate whether something is true or false. They result in a boolean value (True or False in Python).
0
1Array indexing
We’ve also seen that we can access specific portions of arrays with indexing.
[ 0. 20. 40. 60. 80. 100.]We can access individual elements or slices:
x[0]: 0.0x[-1]: 100.0x[2:4]: [40. 60.]Logical indexing
Logical indexing combines these two ideas.
- A logical expression with an array results in a logical array (sometimes called a mask):
logical_array: [False False True False True]- Indexing an array with a logical array returns only the entries of the array where the logical array is
True.
Logical AND/OR with arrays
We can combine logical tests in numpy with the bitwise “AND” operator, &, or the bitwise “OR” operator, |.
The result of logical tests connected by & is only True if BOTH statements are true. The result of logical tests connected by | is True if EITHER statements are true.
Application with related arrays
Logical indexing is particularly powerful with related arrays. For example:
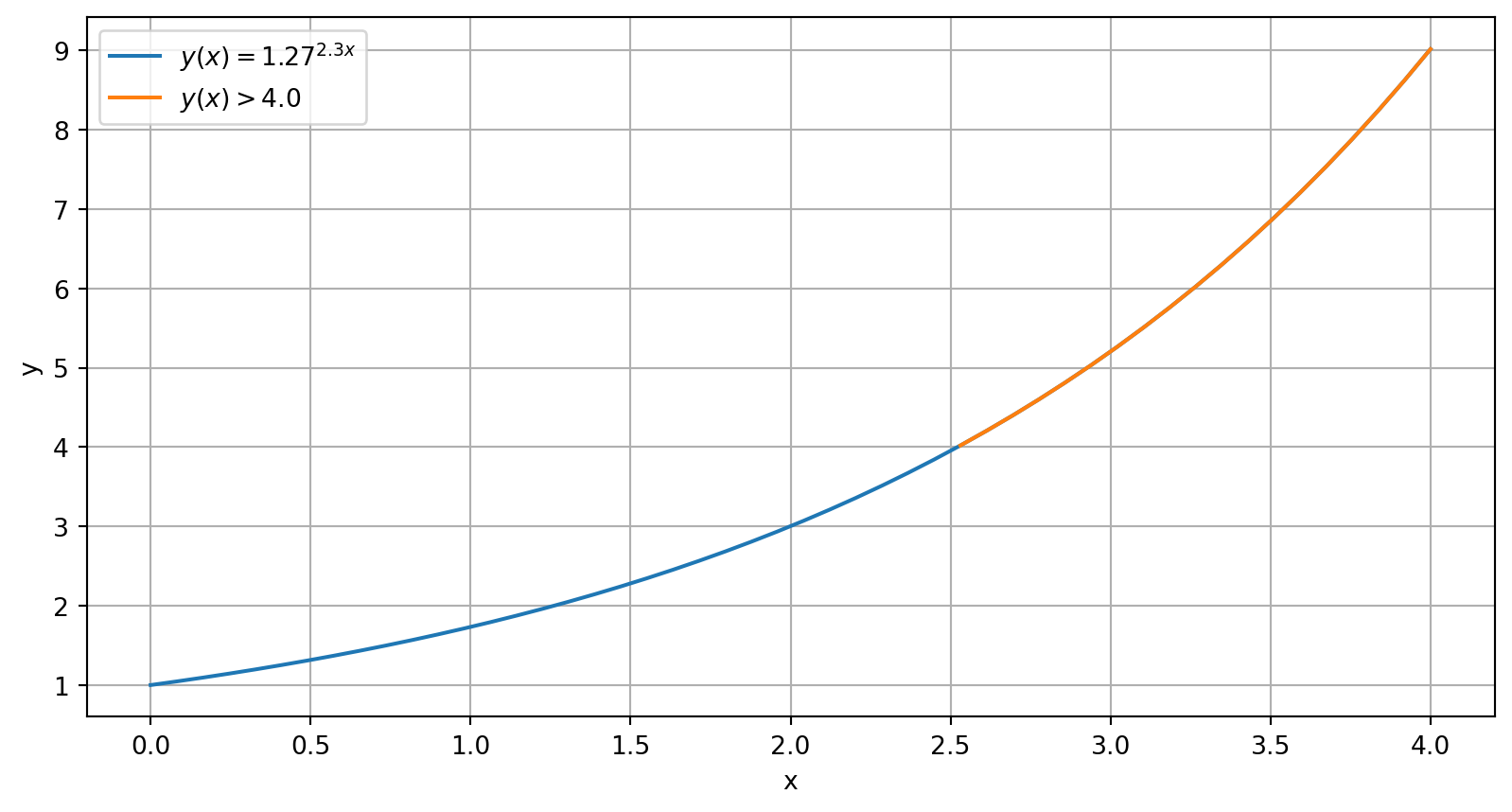
If \(y(x) = 1.27^{2.3x}\), what is the minimum value of \(x\) to result in a value of \(y\) greater than \(4.0\)?
Steps to solving with logical indexing:
- Create a mask using the test condition on \(y\)
- Apply the mask to the related array, \(x\)
- Select the first1 entry in the masked version of \(x\)
Solve with logical array
# Initial arrays x and y:
x = np.linspace(0,4)
y = 1.27**(2.3*x)
# Create a mask using the test condition on y:
logical_mask = y > 4.0
# Apply the mask to the related array, x:
x_masked = x[logical_mask]
# Select the first entry in the masked version of x:
answer = x_masked[0]
print(f"x_masked: {x_masked}")
print(f"answer: {answer:.2f}")x_masked: [2.53061224 2.6122449 2.69387755 2.7755102 2.85714286 2.93877551
3.02040816 3.10204082 3.18367347 3.26530612 3.34693878 3.42857143
3.51020408 3.59183673 3.67346939 3.75510204 3.83673469 3.91836735
4. ]
answer: 2.53What about values of x slightly smaller than 2.53061224?
Plots with masked arrays
See if you can re-create the plots of these array masking examples: (hint: some use np.random.rand())